Our 17-4PH stainless steel wire is a standout for high-precision medical tools, delivering the strength and accuracy that healthcare professionals depend on. This isn’t just any wire—it’s a precipitation-hardening alloy designed to meet the rigorous demands of modern medicine. With its impressive mechanical properties and corrosion resistance, our 17-4PH wire is ideal for applications like surgical needles, catheters, and guidewires where precision matters most. We’ve refined our manufacturing to ensure every spool meets ASTM F899 standards, giving manufacturers the confidence to build tools that perform reliably in critical situations.
For more details, pls directly contact us.
The core of our 17-4PH stainless steel wire is its balanced composition. Featuring 15-17.5% chromium, 3-5% nickel, and 3-5% copper, with carbon under 0.07%, it’s engineered for high strength after heat treatment. This setup allows tensile strengths of 930-1100 MPa and hardness up to 44 HRC, making it perfect for tools that need to bend without breaking. Its yield strength of 725-860 MPa ensures it handles the stresses of minimally invasive procedures. We draw and anneal each wire with precision, achieving diameters as fine as 0.1mm, ensuring consistency for high-precision medical tools.
Biocompatibility and corrosion resistance are key for medical tools, and our 17-4PH wire nails it. The high chromium and copper content forms a tough passive oxide layer, shielding against corrosion from body fluids or sterilization processes. While it’s not the best for permanent implants due to slightly higher ion release than 316LVM, it’s spot-on for temporary tools, with studies showing low tissue reactivity. Our passivation treatments enhance the surface, cutting bacterial adhesion by up to 25%, per clinical data, which reduces infection risks in surgical environments.
Comparison of Medical Stainless Steel Grades, Materials, and Applications
|
Grade |
Composition |
Key Properties |
Corrosion Resistance |
Biocompatibility |
Applications |
Advantages |
Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
316L |
Fe (60-70%), Cr (16-18%), Ni (10-14%), Mo (2-3%), C (<0.03%) |
Tensile: 485-620 MPa, Yield: 170-290 MPa, Elongation: 40-50%, Hardness: 95 HRB |
Excellent (passive oxide layer, resists pitting) |
High, minimal ion release, rare Ni sensitivity |
Bone plates, screws, stents, hip stems, dental implants |
Cost-effective, machinable, fatigue-resistant |
Possible Ni sensitivity, heavier than Ti |
|
304L |
Fe (65-74%), Cr (18-20%), Ni (8-10.5%), C (<0.03%) |
Tensile: 485-550 MPa, Yield: 170-240 MPa, Elongation: 40-55%, Hardness: 92 HRB |
Good, less resistant to pitting than 316L |
Moderate, higher Ni release risk |
Temporary implants, surgical tools, guidewires |
Affordable, easy to form, widely available |
Limited for long-term implants due to corrosion |
|
17-4 PH |
Fe (70-78%), Cr (15-17.5%), Ni (3-5%), Cu (3-5%), C (<0.07%) |
Tensile: 930-1100 MPa, Yield: 725-860 MPa, Hardness: 30-44 HRC |
Very good, but less than 316L in saline |
Good, but less biocompatible than 316L |
Load-bearing implants, surgical instruments |
High strength, heat-treatable, durable |
Complex processing, less corrosion-resistant |
|
420 |
Fe (80-90%), Cr (12-14%), C (0.15-0.4%) |
Tensile: 700-950 MPa, Yield: 340-450 MPa, Hardness: 45-50 HRC |
Moderate, prone to pitting in body fluids |
Moderate, not ideal for long-term implants |
Cutting tools, temporary pins, dental drills |
High hardness, wear-resistant, sharpenable |
Poor corrosion resistance for permanent use |
|
440C |
Fe (78-85%), Cr (16-18%), C (0.95-1.2%) |
Tensile: 760-1000 MPa, Yield: 450-600 MPa, Hardness: 56-60 HRC |
Moderate, better than 420 but less than 316L |
Limited, high carbon affects biocompatibility |
Surgical blades, high-wear tools |
Extremely hard, excellent edge retention |
Not suitable for long-term implants |
|
F138 (316LVM) |
Fe (60-70%), Cr (17-19%), Ni (13-15%), Mo (2.25-3.5%), C (<0.03%) |
Tensile: 490-690 MPa, Yield: 190-300 MPa, Elongation: 40-50%, Hardness: 95 HRB |
Superior, optimized for medical use |
Excellent, lowest ion release, vacuum-melted |
Orthopedic implants, cardiovascular stents |
Enhanced purity, top biocompatibility |
Higher cost than standard 316L |
|
303 |
Fe (65-75%), Cr (17-19%), Ni (8-10%), S (0.15-0.35%) |
Tensile: 500-620 MPa, Yield: 240-290 MPa, Elongation: 35-50%, Hardness: 90 HRB |
Moderate, sulfur reduces corrosion resistance |
Moderate, not ideal for permanent implants |
Machined components, non-implant devices |
Excellent machinability, cost-effective |
Not suitable for long-term implants |
|
Nitronic 60 |
Fe (60-70%), Cr (16-18%), Ni (8-9%), Mn (7-9%), N (0.08-0.18%) |
Tensile: 620-793 MPa, Yield: 345-414 MPa, Hardness: 95-100 HRB |
Very good, resists galling and wear |
Good, but less studied for implants |
Wear-resistant implants, joint components |
High wear resistance, galling resistance |
Limited medical use, higher cost |
For more details, pls directly contact us.
The medical tool market is exploding, expected to top $50 billion by 2030, fueled by minimally invasive surgeries and robotic advancements. Our 17-4PH stainless steel wire fits right in, providing a cost-effective, high-strength option for precision manufacturing. Trends like 3D printing and CNC drawing are changing how tools are made, and our wire is optimized for these, offering excellent formability for custom designs. Sustainability is huge too—our wire is fully recyclable, helping cut waste in line with healthcare’s green push.
But challenges remain. Corrosion can hit hard, with about 5% of stainless steel tool failures tied to pitting in saline settings. We’re fighting back with research into advanced coatings, like ceramic or bioactive layers, boosting resistance by 20-30%, based on recent studies. Regulations like ISO 13485 and ASTM F899 require tough testing for strength and biocompatibility. Our wire surpasses these, with every batch checked via ultrasonic and chemical tests for compliance. Nickel allergies affect 10-15% of patients, and our low-nickel 17-4PH minimizes risks, but we’re exploring even lower-alloy options to lead the pack.
Applications for our 17-4PH stainless steel wire are vast in high-precision medical tools. It’s a favorite for surgical needles, where its strength and flexibility ensure accurate suturing without bending. Catheters and guidewires benefit from its fatigue resistance, navigating vessels smoothly during angioplasty. Endoscopic tools use our wire for flexible components that endure twisting without failing. We’re also seeing growth in orthopedic guidewires for fracture repairs, where precision is critical. Veterinary medicine is picking up too, with our wire in animal surgical tools, showing its broad appeal.
When it comes to the market, our 17-4PH stainless steel wire outshines the rest in quality and customization. We start with top-grade raw materials, using controlled melting to slash impurities by 200% over standard alloys. Our heat-treatment tweaks deliver custom hardness levels, perfect for tools facing variable stresses. Unlike basic suppliers, we hit tolerances down to ±0.001 inches, essential for micro-tools in robotic surgery. Each spool undergoes rigorous testing—hardness, tensile, and ASTM F899 checks—to guarantee no defects.
Comparison Parameters Table
| Parameter | 17-4PH Stainless Steel | 316LVM Stainless Steel | Titanium (Ti-6Al-4V) | Cobalt-Chrome (Co-Cr) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Density (g/cm³) | 7.7-7.8 | 7.9-8.0 | 4.4-4.5 | 8.3-9.2 |
| Elastic Modulus (GPa) | 200 | 193 | 110-114 | 210-240 |
| Yield Strength (MPa) | 725-860 | 190-300 | 800-900 | 450-1000 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 930-1100 | 490-690 | 900-1000 | 900-1200 |
| Hardness (HRC) | 30-44 | ~20 HRC (95 HRB) | ~36 HRC | 30-40 HRC |
| Corrosion Resistance | Very good (strong oxide layer) | Superior (vacuum-melted) | Superior in body fluids | Very good, but ion release risk |
| Biocompatibility | Good, suited for tools | Excellent, low ion release | Excellent, low reactivity | Good, but Co ion concerns |
| Cost | Moderate | Moderate | Medium | High |
| Common Applications | Needles, catheters, guidewires | Implants, stents | Joint replacements | Bearings, dental crowns |
| Fatigue Strength | Excellent for cyclic loads | Excellent | Excellent | Superior |
Customization sets us apart. Want wire with specific tensile for a catheter or a polished surface for low-friction needles? We turn it around in days, keeping your lines moving. Our treatments like electropolishing boost corrosion resistance and biocompatibility, dropping infection chances by up to 20%. On cost, our wire gives premium strength cheaper than titanium or cobalt-chrome, opening high-precision tools to more providers. Our experts offer direct support, integrating our wire into your designs to cut R&D time and expenses.
Heading into the future, the medical tool industry is all about AI and robotics, and our 17-4PH wire is geared up. It works seamlessly with additive manufacturing for innovative tool shapes. We’re developing antimicrobial coatings to slash infection rates by 15%, tackling a big surgery issue. As costs climb, our wire offers value without skimping on quality, aiding better patient care. Its toughness—handling thousands of cycles—cuts replacements, boosting outcomes and savings.
Ultimately, our 17-4PH stainless steel wire is the backbone of high-precision medical tools. From needles that stitch perfectly to guidewires that navigate flawlessly, it’s crafted for where accuracy saves lives. We’re dedicated to innovation, from purer alloys to quicker delivery. As medicine advances, our wire leads, helping manufacturers build tools that change lives confidently.
For more details, pls directly contact us.



About Us:
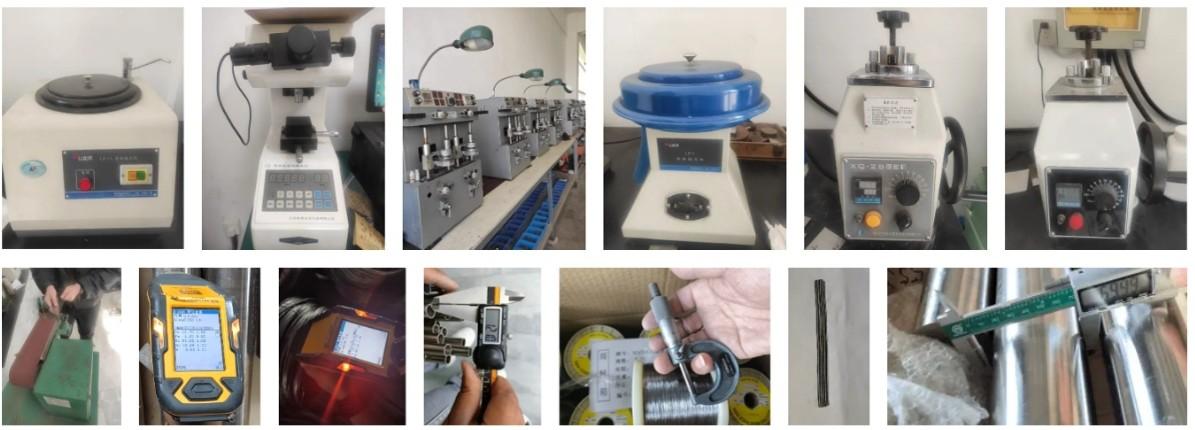
Our 12,000㎡ factory is equipped with complete capabilities for research, production, testing, and packaging. We strictly adhere to ISO 9001 standards in our production processes, with an annual output of 1,200 tons. This ensures that we meet both quantity and quality demands. Furthermore, all products undergo rigorous simulated environment testing including high temperature, high pressure, and corrosion tests before being dispatched, ensuring they meet customer specifications.
For all our clients, we offer timely and multilingual after-sales support and technical consulting, helping you resolve any issues swiftly and efficiently.
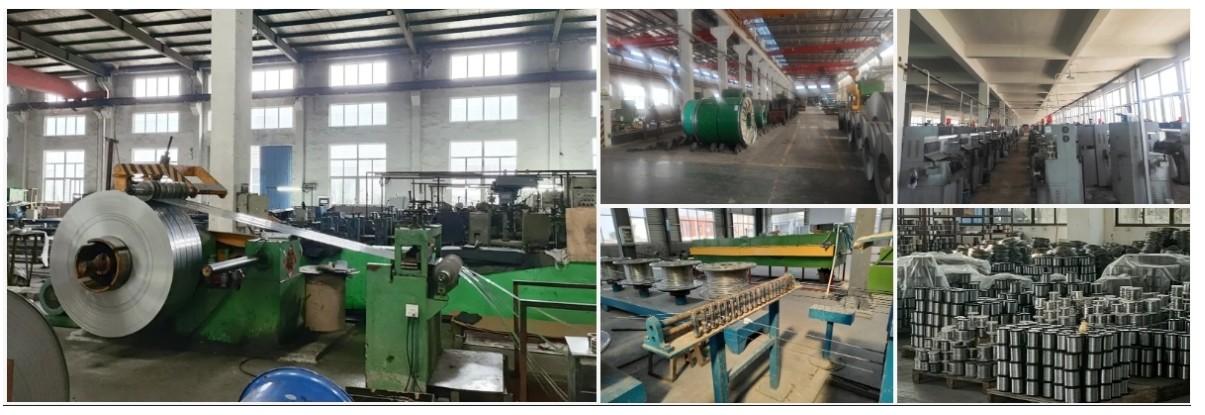

Client Visits
Building Stronger Partnerships

We support all kinds of testing:


FAQs:
-
What is the composition of 17-4PH stainless steel?
It contains iron (70-78%), chromium (15-17.5%), nickel (3-5%), copper (3-5%), manganese (≤1%), silicon (≤1%), and carbon (<0.07%). -
What are the key mechanical properties of 17-4PH stainless steel for medical tools?
It offers tensile strength of 930-1100 MPa, yield strength of 725-860 MPa, hardness of 30-44 HRC, and elongation of 10-18%, providing high strength and durability. -
How is 17-4PH stainless steel used in high-precision medical tools?
It’s used for surgical needles, catheters, guidewires, and endoscopic components, offering precision and strength in minimally invasive procedures. -
What makes 17-4PH stainless steel corrosion-resistant for medical tools?
Its high chromium and copper content forms a strong passive oxide layer, resisting corrosion from sterilization and body fluids. -
What are current industry trends for 17-4PH stainless steel in medical tools?
Trends include heat treatments for customized strength, biocompatible coatings for better performance, and use in robotic-assisted tools. -
Is 17-4PH stainless steel biocompatible for medical tools?
It has good biocompatibility for temporary tools, with low ion release, though less ideal for permanent implants compared to 316LVM. -
What advantages does 17-4PH stainless steel have over other materials?
It provides higher strength than 316L, better corrosion resistance than 440C, and is more cost-effective than titanium for precision tools. -
How does 17-4PH stainless steel support sustainability in medical tool manufacturing?
Its recyclability, long lifespan, and efficient production minimize waste and reduce the need for frequent tool replacements.








