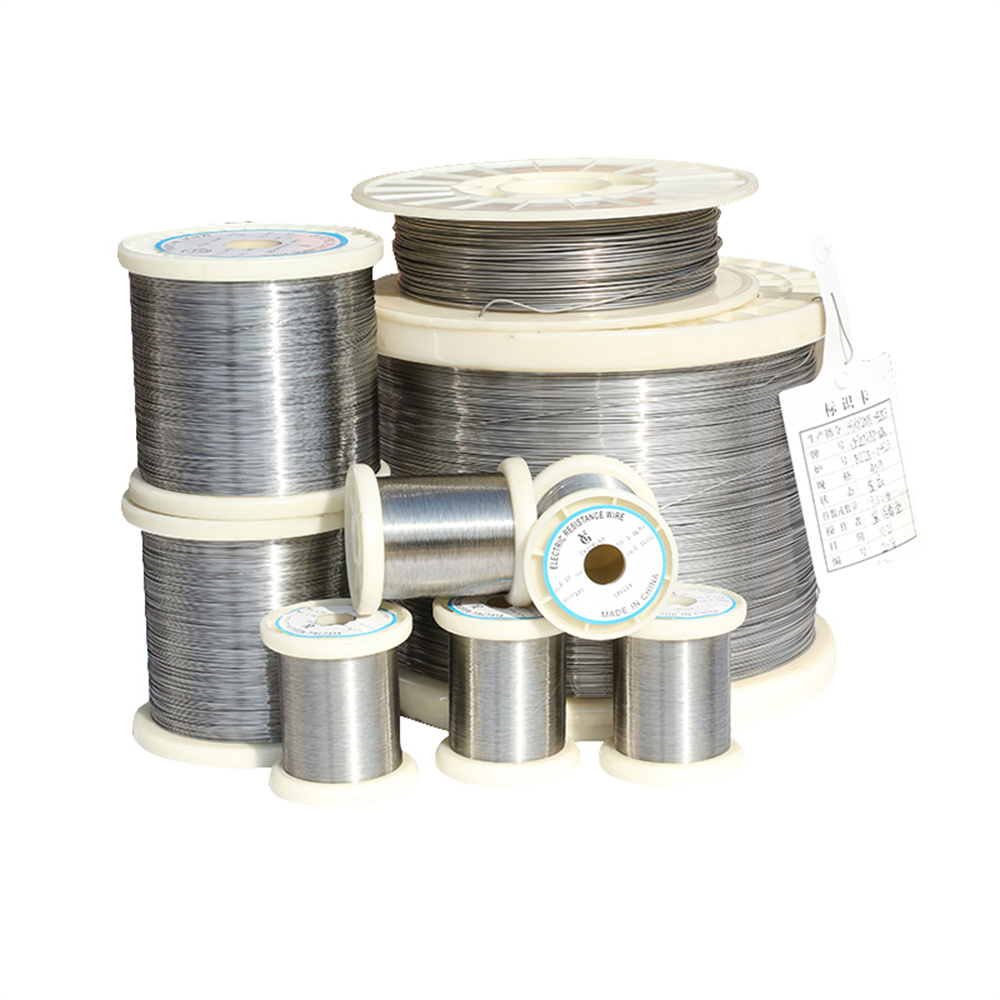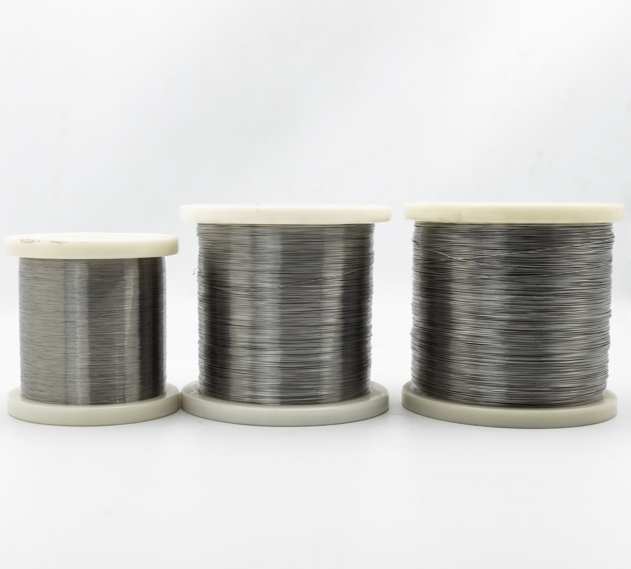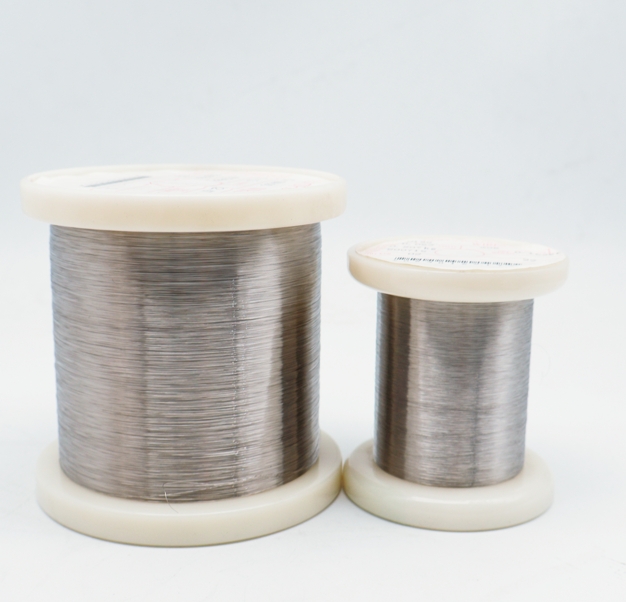
Our electropolished 316L stainless steel wire is a top-tier choice for catheter components, delivering the precision and reliability that medical professionals rely on. This isn’t just any wire—it’s a medical-grade alloy engineered for exceptional performance in minimally invasive procedures. With its superior corrosion resistance and smooth surface, our 316L wire is perfect for crafting guidewires, braiding, and structural elements that ensure catheters navigate the body with ease. We’ve optimized our production to meet ASTM F138 standards, ensuring every spool supports the creation of devices that improve patient outcomes.
For more details, pls directly contact us.
The strength of our 316L stainless steel wire lies in its carefully crafted composition. Packed with 16-18% chromium, 10-14% nickel, and 2-3% molybdenum, with carbon below 0.03%, it’s designed to resist corrosion while staying flexible. Its tensile strength of 485-620 MPa and elongation of 40-50% make it ideal for catheter components that need to bend without breaking. The yield strength of 170-290 MPa ensures it handles the stresses of navigating blood vessels. Our electropolishing process creates a mirror-smooth surface, and we draw wires to diameters as fine as 0.05mm, perfect for the precision demands of catheter manufacturing.
Biocompatibility and corrosion resistance are critical for catheters, and our 316L wire shines. The high chromium and molybdenum content forms a robust passive oxide layer that resists pitting in the body’s saline or acidic fluids. This layer self-heals if scratched, ensuring components remain stable during procedures. Studies show nickel release is low, below 0.5 µg/cm²/week, minimizing risks of allergic reactions, though rare sensitivities can occur. Our electropolishing reduces bacterial adhesion by up to 30%, per clinical data, lowering infection risks in catheter-based interventions.
Comparison of Medical Stainless Steel Grades, Materials, and Applications
|
Grade |
Composition |
Key Properties |
Corrosion Resistance |
Biocompatibility |
Applications |
Advantages |
Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
316L |
Fe (60-70%), Cr (16-18%), Ni (10-14%), Mo (2-3%), C (<0.03%) |
Tensile: 485-620 MPa, Yield: 170-290 MPa, Elongation: 40-50%, Hardness: 95 HRB |
Excellent (passive oxide layer, resists pitting) |
High, minimal ion release, rare Ni sensitivity |
Bone plates, screws, stents, hip stems, dental implants |
Cost-effective, machinable, fatigue-resistant |
Possible Ni sensitivity, heavier than Ti |
|
304L |
Fe (65-74%), Cr (18-20%), Ni (8-10.5%), C (<0.03%) |
Tensile: 485-550 MPa, Yield: 170-240 MPa, Elongation: 40-55%, Hardness: 92 HRB |
Good, less resistant to pitting than 316L |
Moderate, higher Ni release risk |
Temporary implants, surgical tools, guidewires |
Affordable, easy to form, widely available |
Limited for long-term implants due to corrosion |
|
17-4 PH |
Fe (70-78%), Cr (15-17.5%), Ni (3-5%), Cu (3-5%), C (<0.07%) |
Tensile: 930-1100 MPa, Yield: 725-860 MPa, Hardness: 30-44 HRC |
Very good, but less than 316L in saline |
Good, but less biocompatible than 316L |
Load-bearing implants, surgical instruments |
High strength, heat-treatable, durable |
Complex processing, less corrosion-resistant |
|
420 |
Fe (80-90%), Cr (12-14%), C (0.15-0.4%) |
Tensile: 700-950 MPa, Yield: 340-450 MPa, Hardness: 45-50 HRC |
Moderate, prone to pitting in body fluids |
Moderate, not ideal for long-term implants |
Cutting tools, temporary pins, dental drills |
High hardness, wear-resistant, sharpenable |
Poor corrosion resistance for permanent use |
|
440C |
Fe (78-85%), Cr (16-18%), C (0.95-1.2%) |
Tensile: 760-1000 MPa, Yield: 450-600 MPa, Hardness: 56-60 HRC |
Moderate, better than 420 but less than 316L |
Limited, high carbon affects biocompatibility |
Surgical blades, high-wear tools |
Extremely hard, excellent edge retention |
Not suitable for long-term implants |
|
F138 (316LVM) |
Fe (60-70%), Cr (17-19%), Ni (13-15%), Mo (2.25-3.5%), C (<0.03%) |
Tensile: 490-690 MPa, Yield: 190-300 MPa, Elongation: 40-50%, Hardness: 95 HRB |
Superior, optimized for medical use |
Excellent, lowest ion release, vacuum-melted |
Orthopedic implants, cardiovascular stents |
Enhanced purity, top biocompatibility |
Higher cost than standard 316L |
|
303 |
Fe (65-75%), Cr (17-19%), Ni (8-10%), S (0.15-0.35%) |
Tensile: 500-620 MPa, Yield: 240-290 MPa, Elongation: 35-50%, Hardness: 90 HRB |
Moderate, sulfur reduces corrosion resistance |
Moderate, not ideal for permanent implants |
Machined components, non-implant devices |
Excellent machinability, cost-effective |
Not suitable for long-term implants |
|
Nitronic 60 |
Fe (60-70%), Cr (16-18%), Ni (8-9%), Mn (7-9%), N (0.08-0.18%) |
Tensile: 620-793 MPa, Yield: 345-414 MPa, Hardness: 95-100 HRB |
Very good, resists galling and wear |
Good, but less studied for implants |
Wear-resistant implants, joint components |
High wear resistance, galling resistance |
Limited medical use, higher cost |
For more details, pls directly contact us.
The catheter market is booming, projected to hit $70 billion by 2030, driven by rising demand for minimally invasive surgeries and advancements in interventional cardiology. Our 316L stainless steel wire is a key player, offering a cost-effective, high-performance solution for component manufacturing. Industry trends are leaning toward thinner, more flexible catheters and antimicrobial coatings to reduce complications. Our wire’s formability makes it ideal for 3D printing and CNC braiding, enabling custom designs. Sustainability is a priority too—our wire is 100% recyclable, cutting waste and aligning with healthcare’s green initiatives.
Challenges in the industry include corrosion, with 5-7% of stainless steel component failures linked to prolonged exposure to body fluids. We’re addressing this with research into advanced coatings, like heparin or polymer layers, that boost corrosion resistance and hemocompatibility by 20%, based on recent studies. Regulatory standards, like FDA and ISO 13485, demand rigorous testing for biocompatibility and fatigue resistance. Our wire exceeds these, with every batch undergoing ultrasonic testing, chemical analysis, and ASTM F138 compliance checks to ensure zero defects. Nickel allergies affect 10-15% of patients, and while our 316L wire contains nickel, its optimized composition minimizes release, ensuring safety for most applications.
Applications for our 316L stainless steel wire are vital in catheter manufacturing. It’s perfect for guidewires, providing the flexibility and strength needed to navigate complex vascular paths during angioplasty or stent placement. Braided catheter shafts made from our wire enhance kink resistance and torque control, critical for precise interventions. Structural components, like reinforcement coils, benefit from its durability and cost-effectiveness. We’re also seeing use in neurovascular catheters for stroke treatment and in urological catheters, proving its versatility. Veterinary medicine is growing too, with our wire crafting catheter components for animal procedures.
Comparing ourselves to the market, our 316L stainless steel wire stands out for its quality and customization. We source the purest raw materials, reducing impurities by up to 150% compared to standard alloys. Our drawing and electropolishing processes optimize surface smoothness and fatigue resistance, ensuring components perform under cyclic loads. Unlike generic suppliers, we achieve tolerances as tight as ±0.001 inches, ideal for micro-catheter components. Every spool is tested for tensile strength, hardness, and ASTM F138 compliance, guaranteeing reliability in every application.
Customization is our strong suit. Need a wire with a specific diameter for a guidewire or a super-smooth finish for low-friction braiding? We deliver tailored solutions in days, keeping your production on schedule. Our electropolishing and passivation treatments enhance biocompatibility and reduce thrombosis risks by up to 20%. Cost-wise, our 316L wire offers premium performance at a lower price than titanium or cobalt-chrome, making advanced catheters accessible to more hospitals. Our material experts provide hands-on support, helping you integrate our wire into complex designs, saving you time and R&D costs.
Comparison Parameters Table
| Parameter | 316L Stainless Steel | 316LVM Stainless Steel | Titanium (Ti-6Al-4V) | Cobalt-Chrome (Co-Cr) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Density (g/cm³) | 7.9-8.0 | 7.9-8.0 | 4.4-4.5 | 8.3-9.2 |
| Elastic Modulus (GPa) | 193 | 193 | 110-114 | 210-240 |
| Yield Strength (MPa) | 170-290 | 190-300 | 800-900 | 450-1000 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 485-620 | 490-690 | 900-1000 | 900-1200 |
| Hardness (HRB/HRC) | ~95 HRB | ~95 HRB | ~36 HRC | 30-40 HRC |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent (electropolished) | Superior (vacuum-melted) | Superior in body fluids | Very good, but ion release risk |
| Biocompatibility | High, rare Ni sensitivity | Excellent, low ion release | Excellent, low reactivity | Good, but Co ion concerns |
| Cost | Low | Moderate | Medium | High |
| Common Applications | Catheters, guidewires | Stents, implants | Joint replacements | Heart valves, bearings |
| Fatigue Strength | Good for cyclic loads | Excellent | Excellent | Superio |
Looking ahead, the catheter industry is embracing robotics and AI-driven design, and our 316L wire is ready for the future. It’s compatible with additive manufacturing and laser cutting, enabling innovative catheter geometries for patient-specific needs. We’re investing in antimicrobial coatings that could reduce infection rates by 15%, addressing a key concern in catheter procedures. With rising healthcare costs, our wire provides a budget-friendly option without compromising quality, helping clinics deliver better care. Its durability—lasting through countless procedures—reduces replacement needs, improving outcomes and lowering costs.
In short, our electropolished 316L stainless steel wire is a foundation for catheter innovation. From precise guidewires to robust braided shafts, it’s built to perform where reliability and patient safety matter most. We’re committed to pushing the boundaries, whether through cleaner alloys, smarter finishes, or faster delivery. As the catheter field evolves, our wire is at the forefront, enabling manufacturers to create devices that transform lives with confidence.
For more details, pls directly contact us.



About Us:
Our 12,000㎡ factory is equipped with complete capabilities for research, production, testing, and packaging. We strictly adhere to ISO 9001 standards in our production processes, with an annual output of 1,200 tons. This ensures that we meet both quantity and quality demands. Furthermore, all products undergo rigorous simulated environment testing including high temperature, high pressure, and corrosion tests before being dispatched, ensuring they meet customer specifications.
For all our clients, we offer timely and multilingual after-sales support and technical consulting, helping you resolve any issues swiftly and efficiently.

Client Visits
Building Stronger Partnerships

We support all kinds of testing:


FAQs:
-
What is the composition of 316L stainless steel?
It contains iron (60-70%), chromium (16-18%), nickel (10-14%), molybdenum (2-3%), and carbon (<0.03%), with trace manganese, silicon, and sulfur. -
What are the key mechanical properties of 316L stainless steel for catheter components?
Tensile strength ranges from 485-620 MPa, yield strength from 170-290 MPa, elongation from 40-50%, and hardness around 95 HRB, ensuring flexibility and durability. -
How is 316L stainless steel wire used in catheter components?
It’s used for guidewires, braiding, and structural elements in catheters, providing strength and corrosion resistance for precise navigation in medical procedures. -
What makes electropolished 316L stainless steel corrosion-resistant for catheters?
Its high chromium and molybdenum content, enhanced by electropolishing, forms a robust oxide layer, resisting corrosion in body fluids and sterilization processes. -
What are current industry trends for 316L stainless steel in catheter components?
Trends include antimicrobial coatings, 3D printing for custom designs, and development of thinner, more flexible wires for minimally invasive procedures. -
Is 316L stainless steel biocompatible for catheter components?
Yes, it’s highly biocompatible with low ion release, suitable for temporary and short-term implants, though rare nickel sensitivity may occur. -
What advantages does 316L stainless steel have over other materials?
It’s more cost-effective than titanium, with superior corrosion resistance compared to 304 stainless steel, and easier to machine than cobalt-chrome. -
How does 316L stainless steel support sustainability in catheter manufacturing?
Its recyclability, durability, and efficient production reduce waste and the need for frequent replacements, aligning with eco-friendly medical trends.







