Pure nickel sheet and plate have maintained a very solid position in industrial material selection for decades. While many modern alloys promise specialized performance, commercially pure nickel continues to solve a wide range of engineering challenges in a simple, reliable way. Under DIN 17740, grades 2.4066 and 2.4068 represent well-known pure nickel materials designed for demanding environments, particularly where heat resistance and alkali corrosion resistance are critical.
From a DLX company perspective, pure nickel is not viewed as a basic commodity metal. It is a high-performance engineering material with unique advantages that remain difficult to replace in many real-world applications. Industries that operate under aggressive chemical exposure, elevated temperatures, or strict conductivity requirements still rely heavily on pure nickel sheet and plate.
For more details, pls directly contact us.
DIN 17740 defines technical delivery conditions for wrought nickel materials. Within this framework, material numbers 2.4066 and 2.4068 correspond to commercially pure nickel grades that are widely used across Europe and internationally.
Although they are both considered pure nickel, their compositions are adjusted slightly to optimize performance:
-
2.4066 is typically associated with Nickel 200 –type chemistry
-
2.4068 is comparable to Nickel 201 with lower carbon content
The difference lies mainly in carbon levels. Lower carbon improves structural stability at elevated temperatures and reduces the risk of embrittlement during long-term heat exposure. In practical engineering decisions, this distinction becomes important when equipment must operate continuously at higher temperatures.
These grades are valued for their consistent and predictable properties rather than extreme specialization. That balance is precisely why they remain relevant across multiple industries.
Key Material Characteristics of Pure Nickel Sheet and Plate
| Grade | Nickel (Ni)+ Cobalt (Co) | Copper (Cu) | Silicon (Si) | Manganese (Mn) | Carbon (C) | Magnesium (Mg) | Sulfur (S) | Phosphorus (P) | Iron (Fe) |
|
|
99.9% | ≤0.015 | ≤0.03 | ≤0.002 | ≤0.01 | ≤0.01 | ≤0.001 | ≤0.001 | ≤0.04 |
|
|
99.6% | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.05 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.005 | 0.002 | 0.1 |
Physical & Mechanical Properties
| Grades | N4/Ni201 | N6/Ni200 |
| Density | 8.9g/cm³ | 8.9g/cm³ |
| Melting Point | 1455°C | 1445-1470℃ |
| Coefficient of Thermal Expansion | 13.0µm/m·°C | 13.3×10⁻⁶/℃ |
| Thermal Conductivity | 10.1W/m·K | 90.7 W/m·K |
| Electrical Resistivity | 0.103×10⁻⁶Ω·/m (at 20℃) | |
| Electrical Conductivity | 14.6% IACS | |
| Tensile Strength | ≥450MPa | ≥450 MPa |
| Yield Strength | ≥200MPa | ≥150 MPa |
| Elongation at Break | ≥40% | ≥40% |
| Hardness | ≤150 |

For more details, pls directly contact us.
Pure nickel offers a combination of properties that directly address common industrial problems:
-
Excellent resistance to caustic alkalis
-
Strong performance in neutral and mildly reducing environments
-
Good oxidation resistance at elevated temperatures
-
High thermal conductivity
-
High electrical conductivity
-
Stable microstructure
-
Good ductility and formability
-
Reliable weldability
Unlike complex alloy systems, pure nickel derives its performance primarily from the intrinsic stability of nickel itself. This results in predictable behavior during fabrication and long-term service.
Heat and alkali resistance are particularly important. Many materials perform well in one of these conditions but struggle in the other. Pure nickel manages both effectively, making it extremely useful for chemical and thermal systems.
Heat Resistance: Why Pure Nickel Still Matters
In high-temperature environments, material degradation mechanisms such as oxidation, scaling, and microstructural instability become major concerns. Pure nickel sheet and plate, particularly low-carbon variants like 2.4068, maintain good mechanical stability and resist oxidation under many service conditions.
While pure nickel is not intended to compete with high-temperature superalloys in extreme environments, it performs exceptionally well within a broad mid-range temperature window that covers many industrial processes. This includes:
-
Heat exchangers
-
Thermal processing equipment
-
Furnace components
-
High-temperature chemical systems
-
Controlled atmosphere environments
One practical advantage is metallurgical stability. Reduced carbon content helps prevent unwanted phase transformations or carbide-related issues during prolonged heat exposure. This translates into longer service life and fewer unexpected failures.
Alkali Resistance: A Defining Advantage
One of the most widely recognized strengths of pure nickel is its resistance to strong alkaline media. In applications involving sodium hydroxide, potassium hydroxide, and similar caustic solutions, nickel consistently demonstrates superior corrosion resistance compared to many stainless steels and other metals.
Typical alkali-related uses include:
-
Caustic soda production equipment
-
Alkali storage systems
-
Chemical reaction vessels
-
Process piping and linings
-
Electrochemical systems
Corrosion failure in alkali environments is not a minor inconvenience. It often results in safety hazards and significant operational costs. This is why pure nickel sheet and plate remain standard choices in many chemical facilities.
Comparison of DIN 17740 Grades 2.4066 vs 2.4068
Although both materials belong to the pure nickel family, selecting the correct grade ensures optimal performance.
| Property | DIN 2.4066 | DIN 2.4068 |
|---|---|---|
| Nickel Content | High purity | High purity |
| Carbon Content | Higher | Very Low |
| Heat Resistance | Good | Improved at high temp |
| Alkali Resistance | Excellent | Excellent |
| Electrical Conductivity | High | High |
| Thermal Conductivity | Excellent | Excellent |
| Mechanical Stability | Very Good | Very Good |
| Preferred Applications | General industrial use | Elevated temperature service |
In general, 2.4066 fits most standard corrosion-resistant applications. 2.4068 becomes the preferred option when higher operating temperatures or prolonged heat exposure are involved.
Fabrication Benefits of Pure Nickel Sheet and Plate
From a manufacturing standpoint, pure nickel offers several practical advantages. Materials that perform well in service but create difficulties during fabrication increase overall project costs. Pure nickel is widely appreciated for its:
-
Good formability
-
Stable ductility
-
Predictable bending behavior
-
Reliable weldability
-
Consistent machining response
These characteristics simplify production processes. Fabricators value materials that behave consistently and do not introduce unexpected cracking, distortion, or weld defects.
DLX company production places strong emphasis on dimensional accuracy, flatness, and surface condition. For sheet and plate materials, these factors directly influence customer productivity and downstream processing efficiency.
Industry Trends Supporting Pure Nickel Demand
Despite the availability of advanced alloys, several industrial developments continue to reinforce demand for pure nickel sheet and plate:
Expansion of Chemical Processing Capacity
Growing chemical industries require corrosion-resistant materials for aggressive environments.
Rising Reliability Expectations
Industries increasingly prioritize long equipment life and reduced maintenance cycles.
Energy and Electrochemical Technologies
Nickel’s stability supports its role in hydrogen systems and electrochemical applications.
Process Efficiency Focus
Predictable material behavior reduces fabrication and operational risks.
Pure nickel remains attractive because it offers performance without excessive material complexity. In many cases, it provides the most economical long-term solution when lifecycle cost is considered.
DLX Company Perspective: What Differentiates a Supplier
In theory, pure nickel materials are defined by standards. In reality, buyers quickly discover that supplier quality makes a significant difference. Variations in thickness tolerance, surface finish, internal structure, or impurity levels can directly affect fabrication success and service performance.
From the DLX company standpoint, producing pure nickel sheet and plate involves more than meeting nominal composition requirements. Customers depend on:
-
Stable chemical composition
-
Consistent mechanical properties
-
Reliable flatness and tolerances
-
Clean, defect-free surfaces
-
Flexible sizing and cutting options
-
Batch traceability
Industrial users rarely evaluate materials solely on certificates. Real-world usability — ease of forming, welding behavior, dimensional stability — becomes the true measure of quality.
DLX company focuses heavily on production stability and process control. For customers operating in chemical and thermal industries, consistency is often more valuable than marginal price differences.
For more details, pls directly contact us.


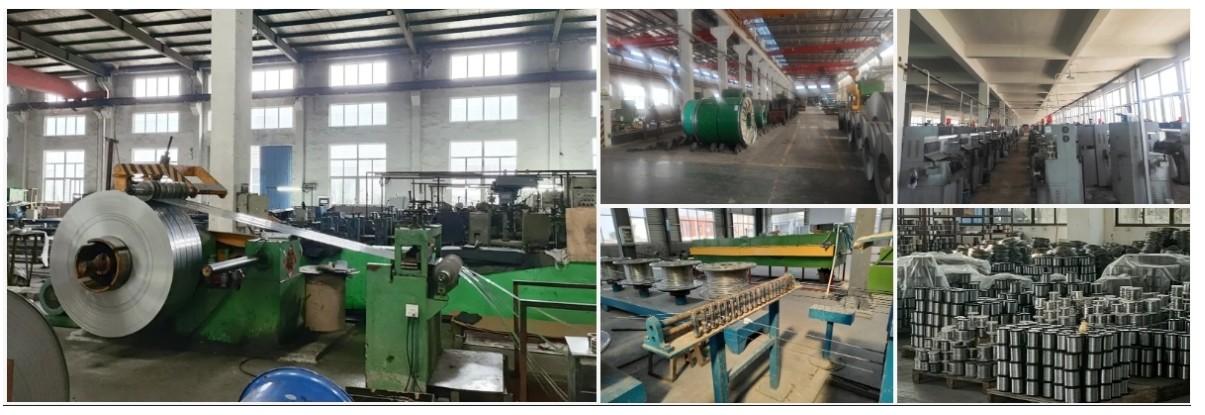
About Us:
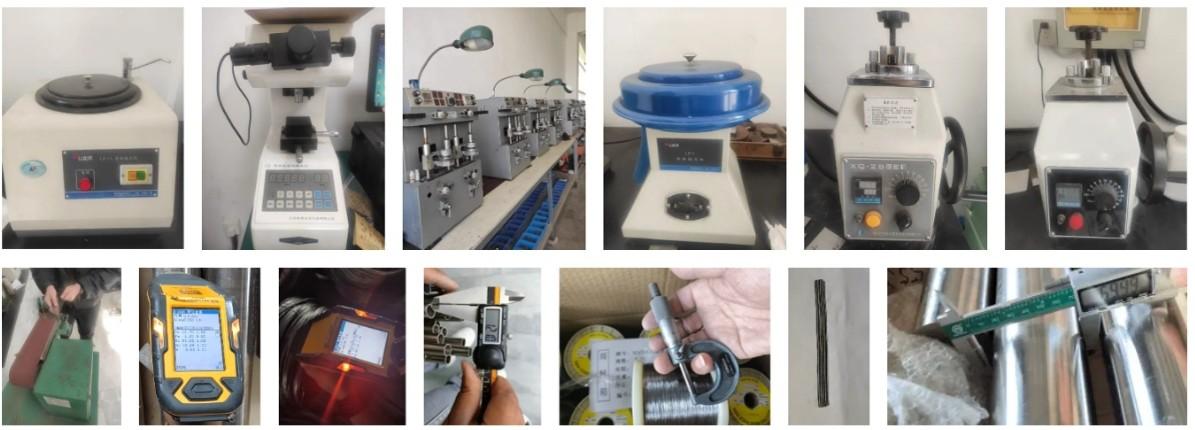
Our 12,000㎡ factory is equipped with complete capabilities for research, production, testing, and packaging. We strictly adhere to ISO 9001 standards in our production processes, with an annual output of 1,200 tons. This ensures that we meet both quantity and quality demands. Furthermore, all products undergo rigorous simulated environment testing including high temperature, high pressure, and corrosion tests before being dispatched, ensuring they meet customer specifications.
For all our clients, we offer timely and multilingual after-sales support and technical consulting, helping you resolve any issues swiftly and efficiently.

Client Visits
Building Stronger Partnerships

We support all kinds of testing:

1. What are DIN 17740 2.4066 and 2.4068 materials?
They are commercially pure nickel grades commonly used for corrosion resistance and thermal stability.
2. What is the main difference between 2.4066 and 2.4068?
Primarily carbon content. 2.4068 has lower carbon and better high-temperature stability.
3. Is pure nickel resistant to strong alkalis?
Yes. Pure nickel is widely known for excellent resistance to caustic alkaline solutions.
4. Can pure nickel sheet be easily fabricated?
Yes. It typically offers good formability and weldability when processed correctly.
5. Why choose pure nickel over stainless steel?
In certain alkali environments, nickel provides superior corrosion resistance.
6. Does temperature affect pure nickel performance?
Yes. Lower carbon grades like 2.4068 perform better at elevated temperatures.
7. Are custom dimensions available?
Yes. Sheet and plate materials can be processed to meet specific project needs.
8. Is pure nickel suitable for electrical applications?
Yes. Its high conductivity makes it useful in various electrical systems.
Final Thoughts
Pure nickel sheet and plate under DIN 17740 continue to be practical, dependable materials for industries facing heat and alkali exposure. Grades 2.4066 and 2.4068 provide engineers with predictable solutions for corrosion resistance, thermal stability, and fabrication reliability.
From a DLX company perspective, supplying pure nickel materials is fundamentally about delivering consistency. Industrial buyers depend on materials that perform not only in service but throughout manufacturing, installation, and long-term operation.