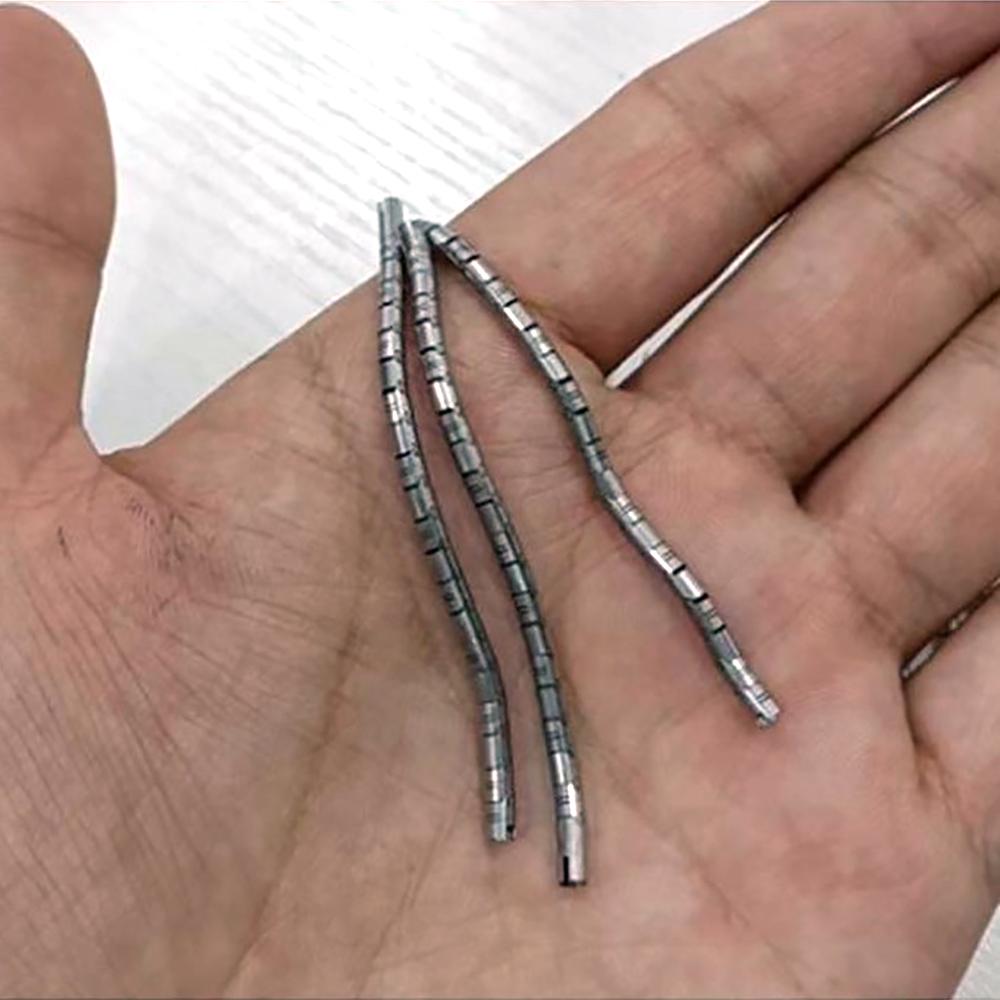
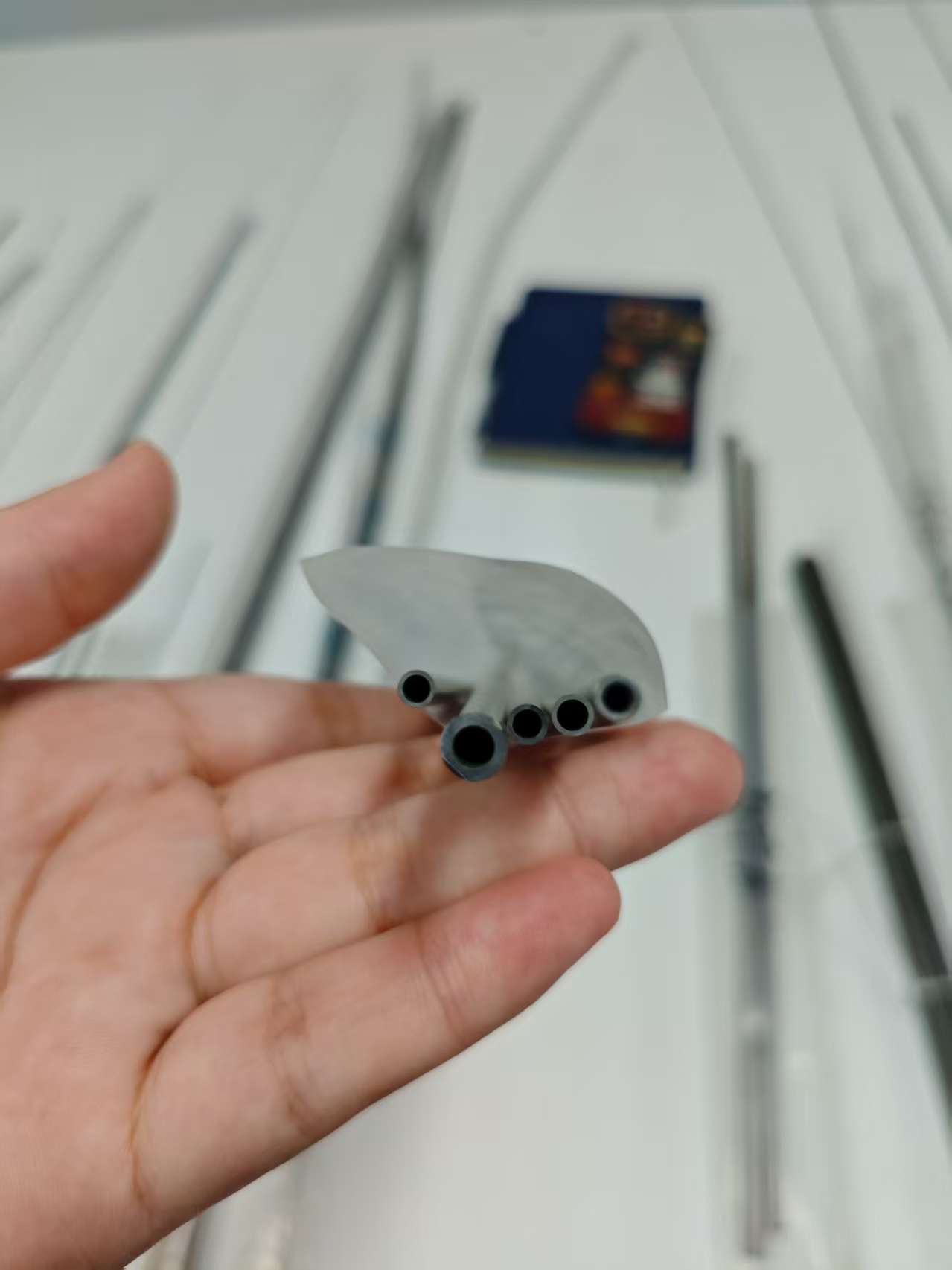
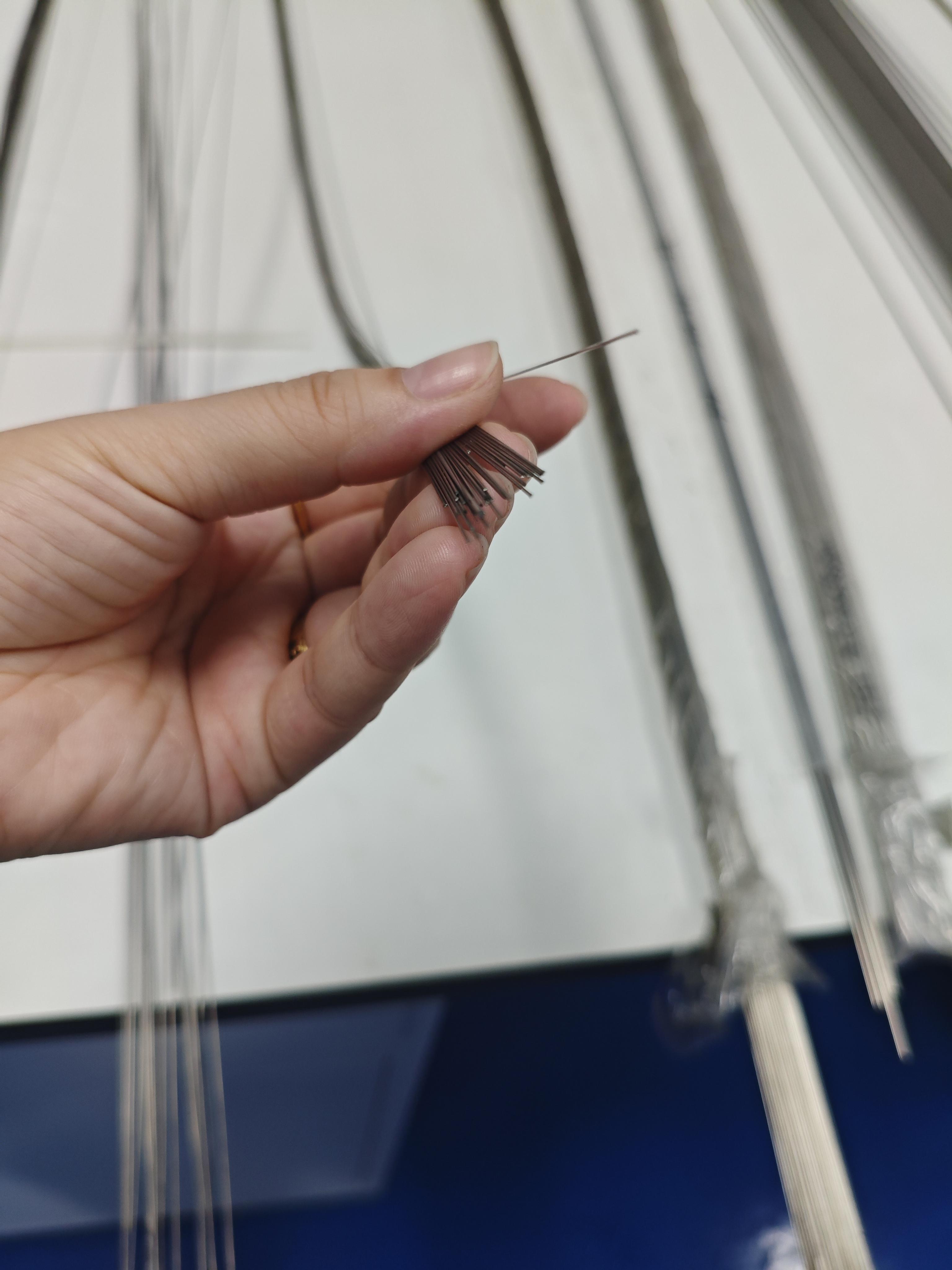
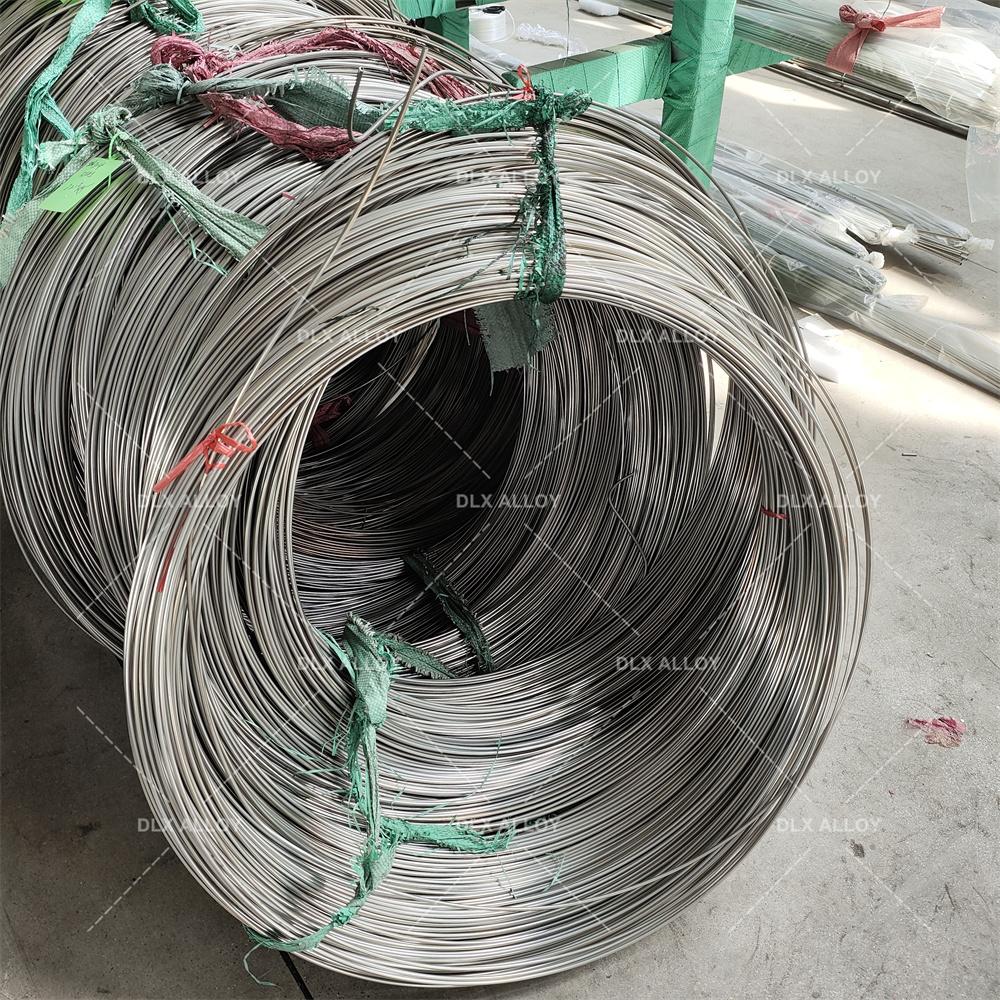
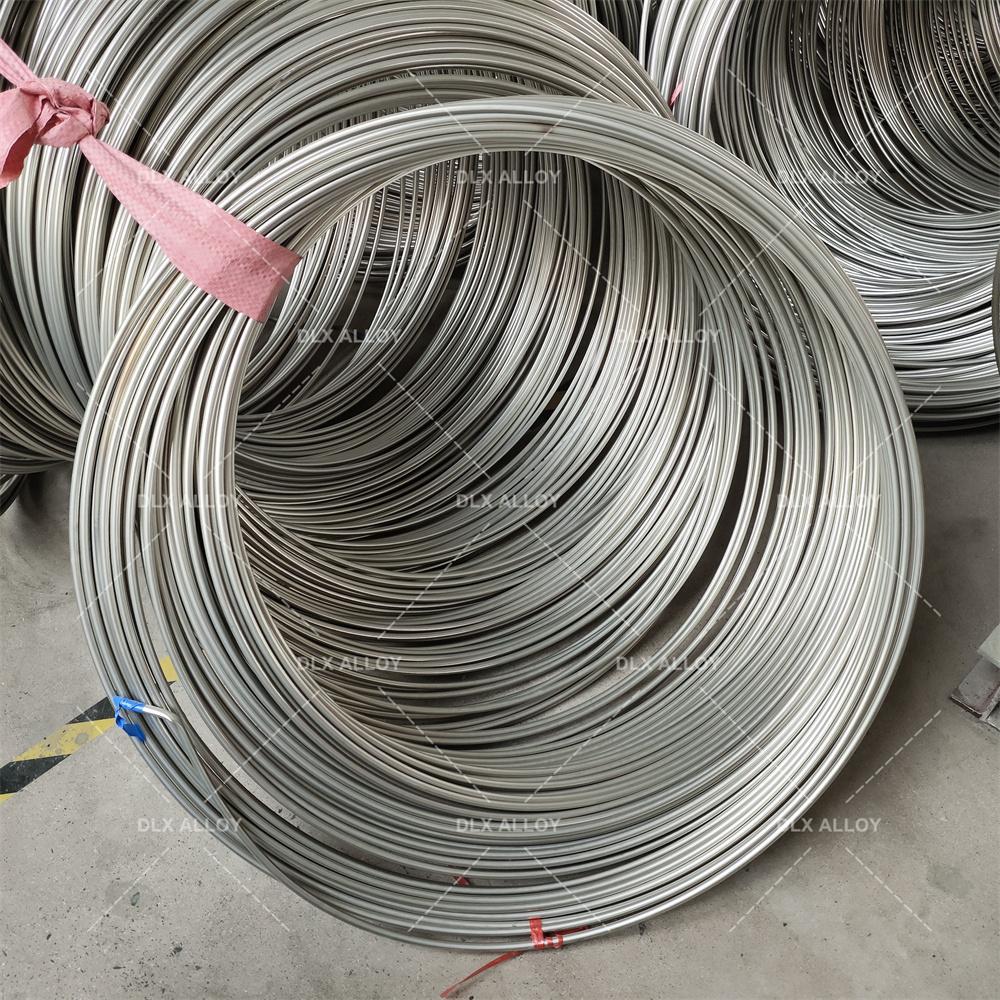
At our company, we’re all about crafting electropolished 316L stainless steel tube for vascular applications that power life-saving procedures like stent placements and catheter insertions. These tubes aren’t just metal—they’re precision-engineered components that help keep blood flowing and hearts beating strong. With a focus on biocompatibility and durability, we’re delivering solutions that cardiologists trust for reliable performance in the toughest vascular environments.
For more details, pls directly contact us.
Let’s dive into what makes our electropolished 316L stainless steel tube for vascular applications a standout. This medical-grade alloy packs 16-18% chromium for a robust corrosion barrier, 10-14% nickel for toughness, and 2-3% molybdenum to resist pitting in the bloodstream’s salty conditions. With carbon kept below 0.03%, it’s weldable and meets ASTM F138 and ISO 5832-1 standards for implants. We produce these tubes in ultra-fine diameters from 0.3mm to 5mm, with walls as thin as 0.05mm, ideal for stents and catheters that navigate tight vessels. Our electropolishing process creates a mirror-smooth Ra <0.15µm finish, reducing thrombus formation and enhancing blood flow compatibility.
Comparison of Medical Stainless Steel Grades, Materials, and Applications
Grade | Composition | Key Properties | Corrosion Resistance | Biocompatibility | Applications | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
316L | Fe (60-70%), Cr (16-18%), Ni (10-14%), Mo (2-3%), C (<0.03%) | Tensile: 485-620 MPa, Yield: 170-290 MPa, Elongation: 40-50%, Hardness: 95 HRB | Excellent (passive oxide layer, resists pitting) | High, minimal ion release, rare Ni sensitivity | Bone plates, screws, stents, hip stems, dental implants | Cost-effective, machinable, fatigue-resistant | Possible Ni sensitivity, heavier than Ti |
304L | Fe (65-74%), Cr (18-20%), Ni (8-10.5%), C (<0.03%) | Tensile: 485-550 MPa, Yield: 170-240 MPa, Elongation: 40-55%, Hardness: 92 HRB | Good, less resistant to pitting than 316L | Moderate, higher Ni release risk | Temporary implants, surgical tools, guidewires | Affordable, easy to form, widely available | Limited for long-term implants due to corrosion |
17-4 PH | Fe (70-78%), Cr (15-17.5%), Ni (3-5%), Cu (3-5%), C (<0.07%) | Tensile: 930-1100 MPa, Yield: 725-860 MPa, Hardness: 30-44 HRC | Very good, but less than 316L in saline | Good, but less biocompatible than 316L | Load-bearing implants, surgical instruments | High strength, heat-treatable, durable | Complex processing, less corrosion-resistant |
420 | Fe (80-90%), Cr (12-14%), C (0.15-0.4%) | Tensile: 700-950 MPa, Yield: 340-450 MPa, Hardness: 45-50 HRC | Moderate, prone to pitting in body fluids | Moderate, not ideal for long-term implants | Cutting tools, temporary pins, dental drills | High hardness, wear-resistant, sharpenable | Poor corrosion resistance for permanent use |
440C | Fe (78-85%), Cr (16-18%), C (0.95-1.2%) | Tensile: 760-1000 MPa, Yield: 450-600 MPa, Hardness: 56-60 HRC | Moderate, better than 420 but less than 316L | Limited, high carbon affects biocompatibility | Surgical blades, high-wear tools | Extremely hard, excellent edge retention | Not suitable for long-term implants |
F138 (316LVM) | Fe (60-70%), Cr (17-19%), Ni (13-15%), Mo (2.25-3.5%), C (<0.03%) | Tensile: 490-690 MPa, Yield: 190-300 MPa, Elongation: 40-50%, Hardness: 95 HRB | Superior, optimized for medical use | Excellent, lowest ion release, vacuum-melted | Orthopedic implants, cardiovascular stents | Enhanced purity, top biocompatibility | Higher cost than standard 316L |
303 | Fe (65-75%), Cr (17-19%), Ni (8-10%), S (0.15-0.35%) | Tensile: 500-620 MPa, Yield: 240-290 MPa, Elongation: 35-50%, Hardness: 90 HRB | Moderate, sulfur reduces corrosion resistance | Moderate, not ideal for permanent implants | Machined components, non-implant devices | Excellent machinability, cost-effective | Not suitable for long-term implants |
Nitronic 60 | Fe (60-70%), Cr (16-18%), Ni (8-9%), Mn (7-9%), N (0.08-0.18%) | Tensile: 620-793 MPa, Yield: 345-414 MPa, Hardness: 95-100 HRB | Very good, resists galling and wear | Good, but less studied for implants | Wear-resistant implants, joint components | High wear resistance, galling resistance | Limited medical use, higher cost |
For more details, pls directly contact us
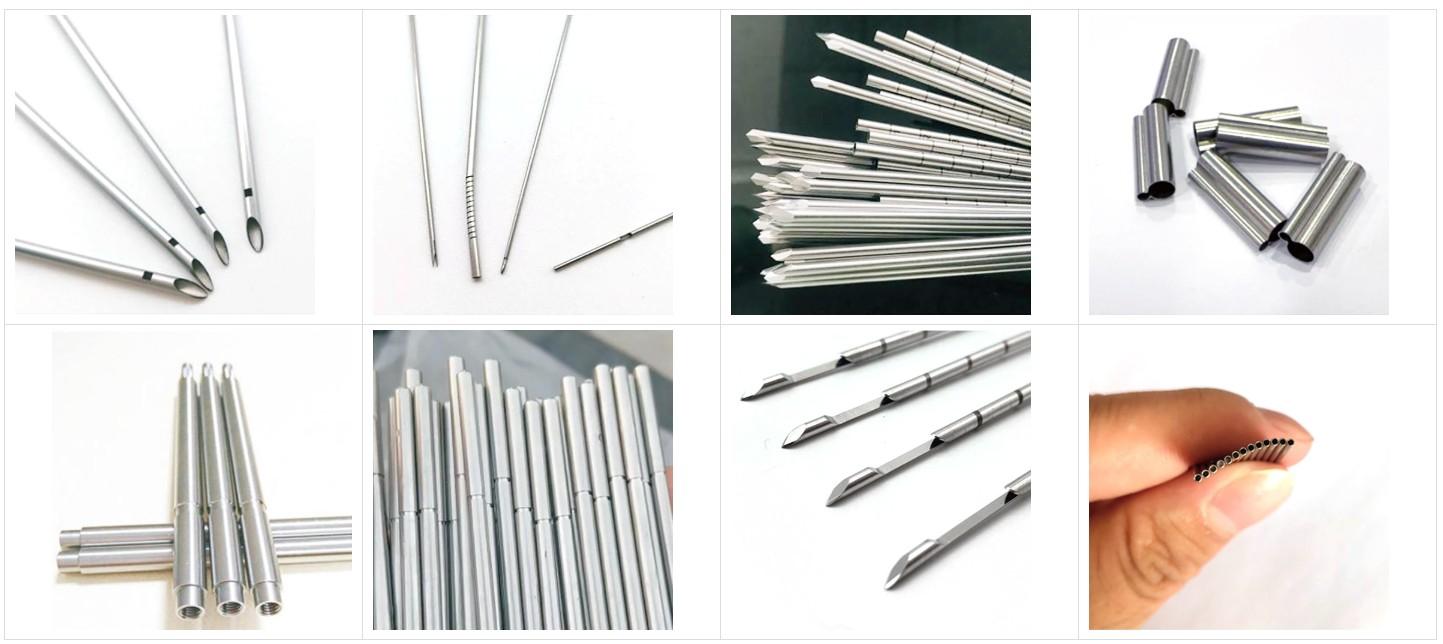

We’re obsessive about precision. Our tubes are cold-drawn to tolerances of ±0.005mm, ensuring seamless integration into balloon-expandable or self-expanding stents. The electropolished surface not only boosts biocompatibility but also supports drug-eluting coatings, cutting restenosis rates by up to 50%. We test for fatigue resistance, simulating millions of arterial pulsations to confirm durability in dynamic environments. Non-magnetic properties make our tubes MRI-safe, a critical feature for post-op imaging. We also offer custom laser-cutting for intricate stent strut patterns, optimizing radial strength for reliable vessel support.
The vascular devices market is thriving, valued at USD 31.2 billion in 2025 and projected to hit USD 50.8 billion by 2032 at a 6.2% CAGR. Cardiovascular diseases are a major driver—over 900 million people globally face heart-related issues, fueled by obesity, diabetes, and aging populations. Minimally invasive procedures like percutaneous coronary interventions (PCI) are now standard, with over 2.5 million stents placed annually. Our electropolished 316L stainless steel tube for vascular applications is built for this, offering the flexibility for catheter delivery and the strength for long-term vessel support.
Regulatory standards are getting stricter, with the FDA and EU MDR demanding robust biocompatibility and traceability data. Our 316L tubes exceed ISO 10993 standards for cytotoxicity and sensitization, ensuring minimal tissue reaction in blood-contact applications. Sustainability is a growing focus—hospitals are pushing for recyclable materials, and stainless steel’s near-100% recyclability makes it a green choice. The medical tubing market is on track to grow from USD 812.59 million in 2025 to USD 1,547.53 million by 2034 at a 6.7% CAGR, with 316L leading for its balance of performance and cost in vascular devices.
Emerging trends are shaping the future. Drug-eluting stents are dominating, with coatings that release anti-proliferative drugs to prevent artery re-narrowing. Bioactive surface treatments, like heparin coatings, are gaining traction to reduce clotting risks. We’re seeing growth in neurovascular stents for aneurysm treatment, where our ultra-precise tubes excel in navigating delicate brain vessels. The rise of transcatheter procedures, like aortic valve replacements (TAVR), is driving demand for reliable tubing, with the TAVR market expected to hit USD 9.7 billion by 2030 at a 7.2% CAGR. Smart stents with sensors for real-time blood flow monitoring are also emerging, and our tubes are ready to integrate with these innovations.
Applications for our electropolished 316L stainless steel tube for vascular applications are wide-ranging. In coronary artery disease, they form the scaffold for stents that push plaque aside, restoring blood flow to prevent heart attacks. For peripheral vascular disease, our tubes are used in stents and catheters for legs or arms, handling higher pressures without collapsing. In neurovascular procedures, they support stents for intracranial aneurysms, offering precision for delicate vessels. They’re also key in embolic protection devices, capturing debris during angioplasty to reduce stroke risks.
Comparison Parameters Table
| Parameter | 316L Stainless Steel (Electropolished) | 304 Stainless Steel | 316LVM Stainless Steel | Cobalt-Chromium Alloy (e.g., L605) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Content (%) | ≤0.03 | ≤0.08 | ≤0.03 | ≤0.15 |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent (Mo, electropolished for blood compatibility) | Good (Cr, less in chlorides) | Superior (vacuum-melted, high purity) | Excellent (Cr, thinner profiles) |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 485-620 | 515-690 | 860-1000 | 1000-1200 |
| Yield Strength (MPa) | 170-310 | 205-310 | 690-860 | 450-650 |
| Biocompatibility | High (smooth surface, low ion release) | Good (short-term use) | Exceptional (minimal inclusions) | High (used in stents, costlier) |
| Density (g/cm³) | 8.0 | 8.0 | 8.0 | 9.1 |
| Magnetic Properties | Non-magnetic | Non-magnetic | Very low permeability | Non-magnetic |
| Cost Effectiveness | Affordable for vascular implants | Most affordable | Premium for purity | Higher, for high-strength needs |
| Common Medical Use | Stents, catheters, guidewires | Surgical instruments | High-purity stents, hypotubes | Stents, where thinner walls matter |
Our tubes shine in drug-eluting stents, providing a smooth base for coatings that release drugs slowly, cutting re-intervention rates. For bifurcation stents in branched arteries, 316L’s ductility allows complex designs without gaps. In acute cases, like myocardial infarctions, our tubes ensure rapid, reliable expansion under pressure. The peripheral vascular devices market, valued at USD 10.4 billion in 2025, is growing at a 6.5% CAGR, highlighting the versatility of 316L in diverse vascular applications.
When it comes to standing out, our company’s approach to electropolished 316L stainless steel tube for vascular applications is unmatched. While standard suppliers might offer generic tubing, we customize with tailored laser-cutting and electropolishing to optimize stent performance, like enhanced radial force for better vessel patency. Our in-house testing is rigorous—corrosion trials in simulated blood environments and finite element analysis predict behavior under arterial stress, ensuring zero failures. This reliability means fewer complications, saving hospitals and patients from costly revisions.
For more details, pls directly contact us.




About Us:
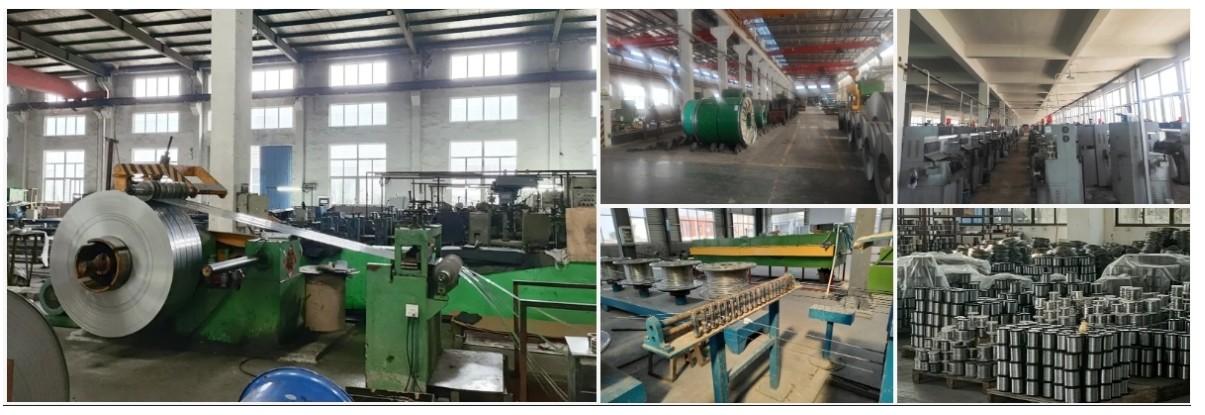
Our 12,000㎡ factory is equipped with complete capabilities for research, production, testing, and packaging. We strictly adhere to ISO 9001 standards in our production processes, with an annual output of 1,200 tons. This ensures that we meet both quantity and quality demands. Furthermore, all products undergo rigorous simulated environment testing including high temperature, high pressure, and corrosion tests before being dispatched, ensuring they meet customer specifications.
For all our clients, we offer timely and multilingual after-sales support and technical consulting, helping you resolve any issues swiftly and efficiently.

Client Visits
Building Stronger Partnerships

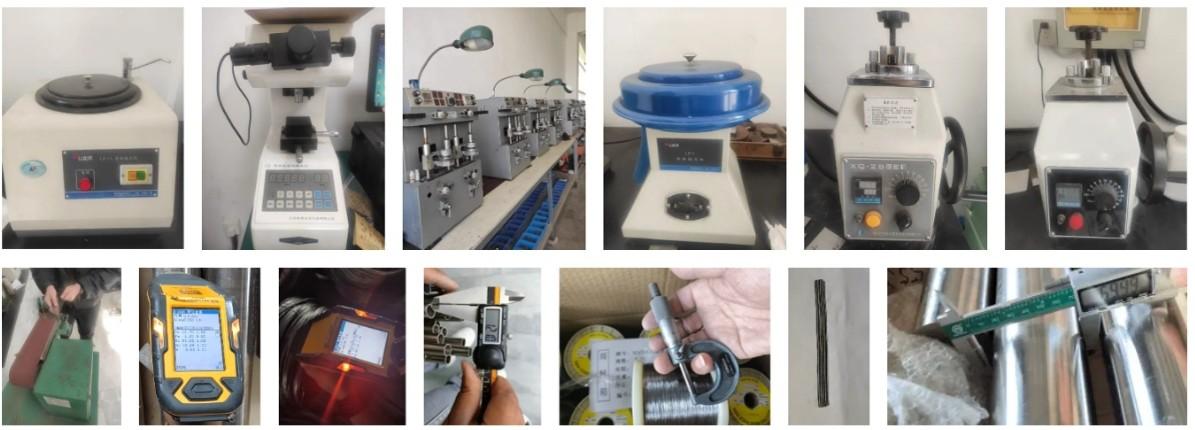
We support all kinds of testing:


FAQs:
Why is electropolished 316L stainless steel ideal for vascular applications?
Electropolished 316L stainless steel offers superior corrosion resistance, enhanced biocompatibility, and a smooth surface to minimize thrombus formation, making it perfect for vascular devices like stents and catheters.What is the material composition of 316L stainless steel for vascular use?
It contains 16-18% chromium, 10-14% nickel, 2-3% molybdenum, and carbon below 0.03%, ensuring excellent corrosion resistance and weldability, compliant with ASTM F138 for medical-grade implants.What are the primary applications of electropolished 316L tubes in vascular devices?
These tubes are used in coronary stents, peripheral vascular catheters, guidewires, and embolic protection devices, enabling precise delivery and reliable performance in blood-contact environments.How do industry trends influence the use of 316L in vascular applications?
The vascular devices market, valued at USD 31.2 billion in 2025, is projected to grow at a 6.2% CAGR to USD 50.8 billion by 2032, driven by rising cardiovascular diseases and minimally invasive procedures.What mechanical properties make electropolished 316L suitable for vascular tubing?
It provides tensile strength of 485-620 MPa, yield strength of 170-310 MPa, elongation over 40%, and high fatigue resistance, ensuring durability in dynamic vascular environments.Is electropolished 316L stainless steel biocompatible for vascular implants?
Yes, it meets ISO 10993 and ASTM F138 standards, with low ion release and a smooth electropolished surface that reduces platelet adhesion, minimizing clotting risks in vascular applications.What emerging trends support electropolished 316L in vascular devices?
Trends include drug-eluting devices, bioactive coatings, and a medical tubing market expected to reach USD 1,547.53 million by 2034 at a 6.7% CAGR, favoring high-purity, smooth-surfaced alloys.How does electropolished 316L handle sterilization for vascular applications?
It withstands autoclaving, gamma irradiation, and ethylene oxide sterilization without surface degradation, maintaining a mirror-like finish for cleanroom production and sterile implantation.