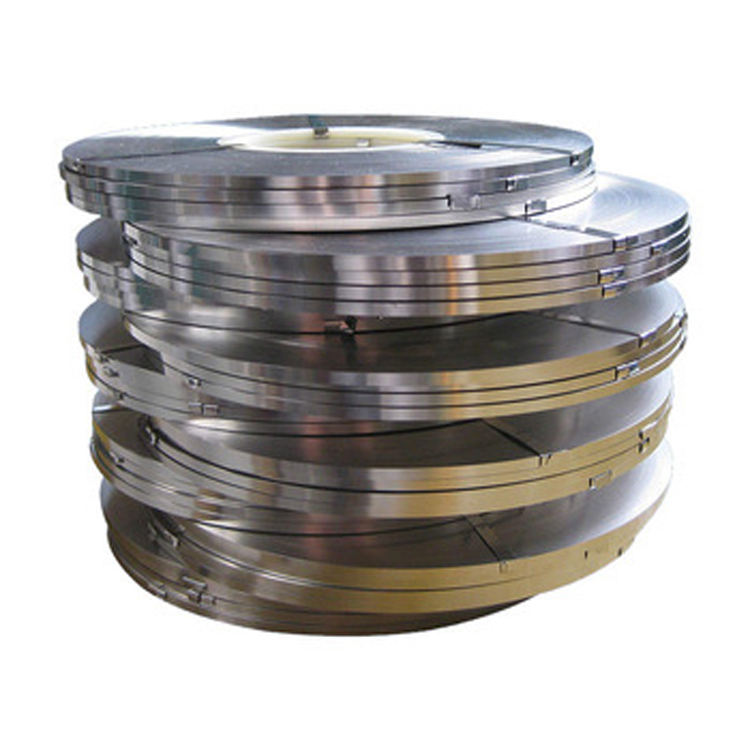
Pure Nickel Strip often looks like a simple semi-finished material, but in many industries, it quietly plays a mission-critical role. When systems operate in corrosive environments, under electrical load, or across temperature fluctuations, material selection stops being a routine purchasing decision and becomes a core engineering choice. This is exactly where corrosion resistant pure nickel strip proves its value, especially in alkaline electrolysis and chemical processing applications.
From a materials perspective, commercially pure nickel offers a unique combination of properties. It delivers strong resistance to alkaline media, stable electrical conductivity, excellent ductility, and predictable mechanical behavior. Unlike many alloyed materials that trade one property for another, pure nickel maintains a balanced performance profile that makes design and manufacturing more straightforward. For engineers and procurement teams alike, that balance reduces risk.
For more details, pls directly contact us.
In alkaline electrolysis systems, chemical stability is everything. Components are continuously exposed to aggressive electrolytes, electrical currents, and sometimes elevated temperatures. Any material degradation can translate into efficiency loss, contamination, or unplanned maintenance. Pure nickel strip addresses these challenges through its natural resistance to alkaline corrosion. The protective oxide layer that forms on nickel surfaces acts as a barrier, slowing down chemical attack and extending service life.
Another practical advantage is electrical performance. Electrolysis processes are inherently electrical, and the current distribution across electrodes, connectors, and conductive paths directly impacts system efficiency. Pure nickel provides high electrical conductivity while also resisting corrosion — a combination that is surprisingly difficult to achieve with many alternative materials. This dual benefit explains why nickel remains a trusted choice in hydrogen-related technologies.
| Grade | Nickel (Ni)+ Cobalt (Co) | Copper (Cu) | Silicon (Si) | Manganese (Mn) | Carbon (C) | Magnesium (Mg) | Sulfur (S) | Phosphorus (P) | Iron (Fe) |
|
|
99.9% | ≤0.015 | ≤0.03 | ≤0.002 | ≤0.01 | ≤0.01 | ≤0.001 | ≤0.001 | ≤0.04 |
|
|
99.6% | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.05 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.005 | 0.002 | 0.1 |
Physical & Mechanical Properties
| Grades | N4/Ni201 | N6/Ni200 |
| Density | 8.9g/cm³ | 8.9g/cm³ |
| Melting Point | 1455°C | 1445-1470℃ |
| Coefficient of Thermal Expansion | 13.0µm/m·°C | 13.3×10⁻⁶/℃ |
| Thermal Conductivity | 10.1W/m·K | 90.7 W/m·K |
| Electrical Resistivity | 0.103×10⁻⁶Ω·/m (at 20℃) | |
| Electrical Conductivity | 14.6% IACS | |
| Tensile Strength | ≥450MPa | ≥450 MPa |
| Yield Strength | ≥200MPa | ≥150 MPa |
| Elongation at Break | ≥40% | ≥40% |
| Hardness | ≤150 |

For more details, pls directly contact us.
Beyond electrolysis, the chemical processing industry imposes its own demanding conditions. Equipment and components must tolerate reactive substances, moisture, and temperature variations. Reliability and consistency matter more than theoretical peak performance. In this context, pure nickel strip functions as a dependable, engineering-friendly solution. Its resistance to many chemical environments, combined with good mechanical formability, allows it to be integrated into a wide range of designs.
Manufacturing considerations further reinforce its appeal. Pure nickel strip is highly ductile, which simplifies stamping, bending, deep drawing, and forming operations. Complex geometries can be produced without excessive cracking or tool wear. For production engineers, this translates into smoother workflows, lower scrap rates, and more predictable yields. In high-volume manufacturing, these practical benefits often outweigh small differences in raw material cost.
Thickness customization is another factor that should not be underestimated. Different applications require very different material behaviors. Thin strips may be selected for precision electronic components or fine connectors, where flexibility and tight tolerances dominate. Thicker strips may be preferred for structural stability or higher current-carrying capacity. A supplier capable of delivering consistent thickness control provides a real operational advantage.
Surface quality also plays a surprisingly important role. Bright, clean nickel surfaces improve weldability, reduce contact resistance, and enhance coating adhesion when required. In resistance welding and electrical joining processes, even minor surface defects can create variability. High-quality rolling, annealing, and finishing processes ensure that the strip behaves consistently during downstream fabrication.
Typical Parameter Comparison – Pure Nickel Strip
| Property / Feature | Pure Nickel Strip (GB/T N6) | General Industrial Expectation |
|---|---|---|
| Nickel Content | ≥ 99.5% (typical) | High-purity nickel |
| Density | ~8.9 g/cm³ | Standard for pure nickel |
| Electrical Conductivity | High | Suitable for electrical uses |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent (especially alkaline) | Critical advantage |
| Ductility | Very good | Ideal for forming/stamping |
| Thickness Range | Customizable (thin to thick) | Application-dependent |
| Surface Condition | Bright / Clean / Annealed | Manufacturing-friendly |
| Weldability | Excellent | Suitable for resistance welding |
From a sourcing perspective, buyers increasingly look beyond simple specifications. Traceability, supply stability, and process control are becoming just as important as nominal chemical composition. A technically competent supplier does more than ship material — it helps reduce uncertainty. Documentation, quality systems, and responsive communication all contribute to smoother procurement and production cycles.
Within this landscape, DLX approaches pure nickel strip manufacturing with a strong emphasis on consistency and application awareness. Instead of treating nickel strip as a generic commodity, production is aligned with the needs of industrial users. Tight thickness tolerances, controlled surface conditions, and stable mechanical properties are prioritized because they directly influence customer outcomes.
Long-term partnerships are also a central theme. Many customers operate in industries where qualification cycles are long and design changes are costly. Consistency between batches, reliable lead times, and technical support become essential. By maintaining stable process controls and quality management practices, DLX supports customers who cannot afford unpredictable material behavior.
Market trends further highlight the relevance of pure nickel strip. Growth in hydrogen technologies, renewable energy systems, advanced batteries, and precision electronics continues to drive demand for corrosion-resistant, conductive materials. While new materials constantly emerge, pure nickel remains firmly established due to its proven reliability and well-understood performance.
Cost efficiency is often discussed, but it should be framed correctly. The real cost of a material includes not only purchase price, but also processing efficiency, durability, maintenance impact, and failure risk. In corrosive and electrically active environments, premature material degradation can easily outweigh any savings from lower-cost alternatives. This is one of the reasons pure nickel strip continues to be selected for critical applications.
Ultimately, the role of pure nickel strip is less about novelty and more about dependable engineering. It offers a rare mix of corrosion resistance, conductivity, formability, and manufacturing compatibility. In alkaline electrolysis and chemical processing industries, where operational stability is non-negotiable, those attributes are not just convenient — they are essential.
For more details, pls directly contact us.


About Us:
Our 12,000㎡ factory is equipped with complete capabilities for research, production, testing, and packaging. We strictly adhere to ISO 9001 standards in our production processes, with an annual output of 1,200 tons. This ensures that we meet both quantity and quality demands. Furthermore, all products undergo rigorous simulated environment testing including high temperature, high pressure, and corrosion tests before being dispatched, ensuring they meet customer specifications.
For all our clients, we offer timely and multilingual after-sales support and technical consulting, helping you resolve any issues swiftly and efficiently.

Client Visits
Building Stronger Partnerships

We support all kinds of testing:

1. What exactly is GB/T N6 pure nickel strip?
GB/T N6 is a widely recognized Chinese designation for commercially pure nickel, typically aligned with high-purity nickel grades used in industrial and electronic applications. It is known for excellent corrosion resistance, stable electrical properties, and very good ductility. In strip form, it is precision rolled to controlled thicknesses for manufacturing and assembly processes.
2. Why is pure nickel strip preferred in corrosive environments?
Pure nickel naturally forms a protective oxide layer that resists many aggressive media, especially alkaline conditions. This makes it highly reliable in chemical processing, alkaline electrolysis, and battery-related environments where long-term material stability is critical.
3. How does thickness customization affect performance?
Thickness directly influences electrical resistance, mechanical flexibility, and forming behavior. Thinner strips are easier to shape and ideal for precision components, while thicker strips offer improved mechanical strength and current-carrying capacity. Proper customization ensures the strip matches the functional requirements of the device or assembly.
4. Is GB/T N6 comparable to other international nickel grades?
Yes. GB/T N6 is commonly considered equivalent to internationally recognized pure nickel grades such as Nickel 200 / Nickel 201 (UNS N02200 / N02201) and DIN 2.4060 / 2.4066. These materials share similar purity levels and core properties, though exact chemistry limits may vary slightly by standard.
5. What industries commonly use pure nickel strip?
Typical industries include battery manufacturing, hydrogen energy systems, resistance welding, electronics, aerospace components, chemical equipment, and precision instrumentation. The combination of conductivity, corrosion resistance, and formability makes it extremely versatile.
6. How important is surface quality for nickel strip?
Surface condition is critical. Bright, clean surfaces improve weldability, conductivity, and coating performance. High-quality rolling and annealing processes minimize defects such as scratches, oxidation, and edge cracking, which directly affect downstream manufacturing efficiency.
7. Can pure nickel strip handle high temperatures?
Pure nickel maintains good mechanical integrity and oxidation resistance at elevated temperatures compared with many common metals. While exact limits depend on application conditions, it performs well in many thermal and electrical systems requiring temperature stability.
8. What factors should buyers evaluate when sourcing nickel strip?
Key considerations include chemical purity, thickness tolerance, surface finish, mechanical properties, supply consistency, and technical support. Reliable suppliers also provide traceability, quality documentation, and flexible production capabilities.