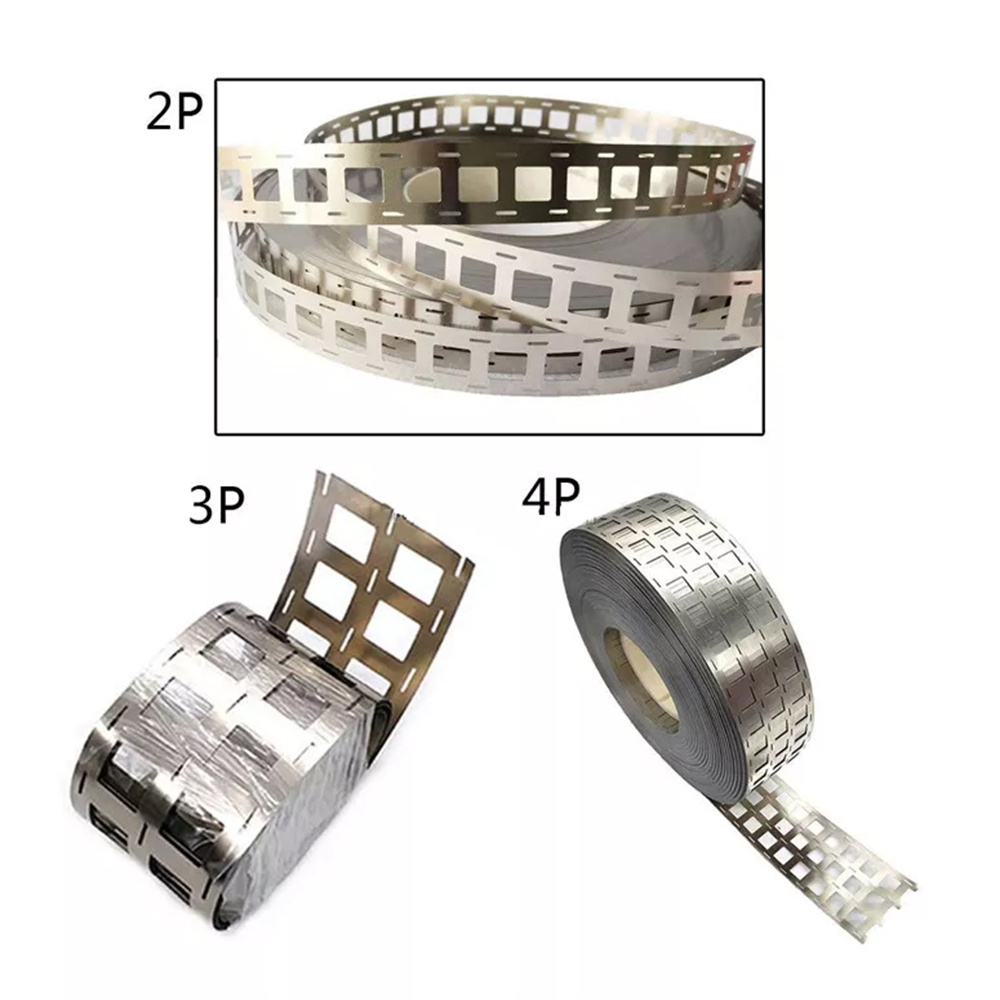
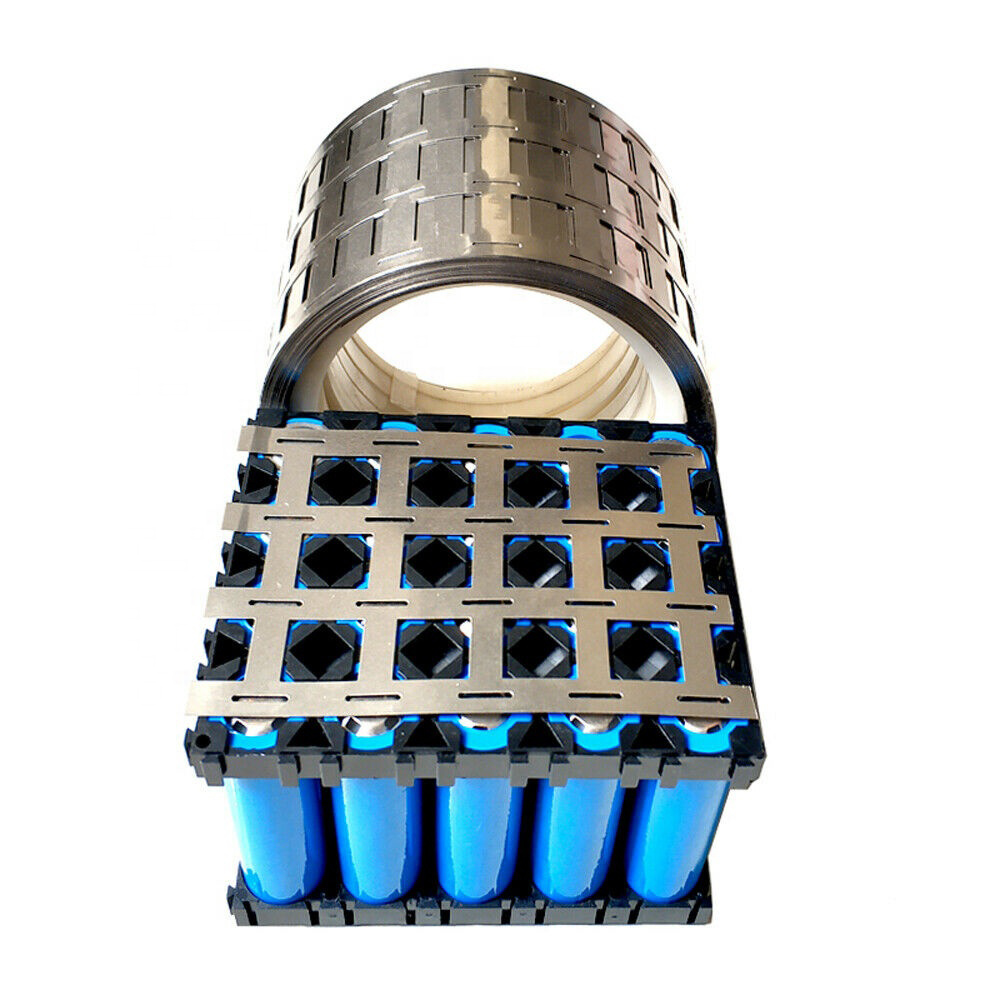
Pure Nickel Strip under DIN 2.4060 and DIN 2.4066 specifications plays a quiet but critical role in precision electronics manufacturing. While it may look like a simple metal material on the surface, its functional importance becomes clear when considering the demands of modern electronic components. In this space, performance margins are tight, tolerances are unforgiving, and reliability is non-negotiable.
Precision electronics are built around consistency. Whether the end product is a connector, lead frame, shielding element, or micro conductive component, every piece must behave predictably. Electrical pathways must remain stable, mechanical deformation must stay within design limits, and assembly processes must run smoothly at scale. This is exactly where high-purity nickel strip stands out.
For more details, pls directly contact us.
DIN 2.4060 and DIN 2.4066 represent two closely related forms of commercially pure nickel. Both grades offer high nickel content, excellent ductility, and dependable conductivity. The subtle differences between them, particularly the lower carbon content of DIN 2.4066, provide engineers with flexibility when balancing thermal stability and mechanical behavior. For precision electronics, these differences translate into practical advantages rather than abstract metallurgical details.
One of the most valued characteristics of pure nickel strip is its forming behavior. Precision components often require intricate shapes, sharp bends, or extremely thin sections. Materials that lack sufficient ductility tend to crack, deform unevenly, or generate high scrap rates. Pure nickel’s inherent softness and workability help minimize these risks, supporting stable high-speed stamping and forming operations.
| Grade | Nickel (Ni)+ Cobalt (Co) | Copper (Cu) | Silicon (Si) | Manganese (Mn) | Carbon (C) | Magnesium (Mg) | Sulfur (S) | Phosphorus (P) | Iron (Fe) |
|
|
99.9% | ≤0.015 | ≤0.03 | ≤0.002 | ≤0.01 | ≤0.01 | ≤0.001 | ≤0.001 | ≤0.04 |
|
|
99.6% | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.05 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.005 | 0.002 | 0.1 |
Physical & Mechanical Properties
| Grades | N4/Ni201 | N6/Ni200 |
| Density | 8.9g/cm³ | 8.9g/cm³ |
| Melting Point | 1455°C | 1445-1470℃ |
| Coefficient of Thermal Expansion | 13.0µm/m·°C | 13.3×10⁻⁶/℃ |
| Thermal Conductivity | 10.1W/m·K | 90.7 W/m·K |
| Electrical Resistivity | 0.103×10⁻⁶Ω·/m (at 20℃) | |
| Electrical Conductivity | 14.6% IACS | |
| Tensile Strength | ≥450MPa | ≥450 MPa |
| Yield Strength | ≥200MPa | ≥150 MPa |
| Elongation at Break | ≥40% | ≥40% |
| Hardness | ≤150 |

For more details, pls directly contact us.
Electrical performance is equally important. In many electronic applications, conductivity must remain consistent across thousands or millions of parts. Variations in alloy composition or microstructure can introduce unpredictable resistance changes, which may compromise signal integrity or thermal performance. High-purity nickel strip offers a stable electrical profile, making it a reliable choice for current-carrying and contact elements.
Corrosion resistance further strengthens its appeal. Electronic devices are not always protected from environmental stress. Humidity, temperature cycling, and chemical exposure can gradually degrade poorly chosen materials. Pure nickel’s resistance to many corrosive influences contributes to longer component life and reduced failure risk, which is especially important for industrial and high-reliability electronics.
Manufacturing compatibility is another key advantage. Precision electronics production often combines multiple processes, including laser cutting, resistance welding, and micro-assembly techniques. Materials that respond inconsistently to heat or pressure complicate process control and increase defect rates. Pure nickel strip’s predictable behavior under welding and thermal conditions simplifies these operations, improving repeatability.
Industry trends continue to reinforce the relevance of pure nickel materials. Miniaturization, higher circuit densities, and the integration of electronics into demanding environments all increase the need for stable conductive metals. At the same time, manufacturers are under pressure to improve yields, reduce waste, and maintain strict quality standards. Materials that naturally support these objectives gain strategic importance.
Comparison of Typical Parameters
| Property / Feature | DIN 2.4060 / 2.4066 Pure Nickel Strip | Generic Nickel Alloy Strip |
|---|---|---|
| Nickel Content | Very high (commercially pure) | Composition varies |
| Electrical Conductivity | Stable and predictable | Alloy dependent |
| Formability | Excellent | May vary |
| Thickness Precision | Tight control possible | Supplier dependent |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent in many environments | Alloy dependent |
| Weldability | Excellent | Varies |
| Suitability for Micro Parts | Very good | Application specific |
| Typical Industries | Precision electronics, batteries, energy systems | Broader industrial uses |
In this context, the choice of supplier becomes more than a purchasing decision. Precision electronics production is highly sensitive to material variation. Even minor inconsistencies in thickness, surface condition, or mechanical properties can disrupt automated equipment or alter product performance. A reliable supplier therefore contributes directly to manufacturing stability.
From the DLX company perspective, supplying DIN 2.4060 and DIN 2.4066 pure nickel strip is not treated as a commodity business. The emphasis is placed on process discipline, quality control, and real-world usability. Maintaining consistent purity, controlling rolling parameters, and ensuring dimensional precision are fundamental priorities rather than optional features.
Thickness accuracy is particularly critical. Precision electronics frequently require tight tolerances to maintain mechanical fit and electrical behavior. Variations that may seem negligible in general industrial contexts can become significant at micro scales. Through controlled production and inspection practices, DLX focuses on delivering strip that behaves consistently during forming and assembly.
Surface quality also matters. Clean, uniform surfaces contribute to reliable welding, stable contact resistance, and reduced contamination risks. In high-volume electronics manufacturing, surface defects can cascade into assembly issues or long-term reliability concerns. Controlled finishing and handling procedures help ensure that the nickel strip meets these practical expectations.
Customization capability is another essential aspect. Precision electronics applications vary widely in geometry, thickness, and temper requirements. Standard dimensions may not always align with specialized production lines. Flexible manufacturing allows DLX to provide tailored solutions, supporting both design optimization and procurement efficiency.
Beyond material properties, supply reliability carries significant weight. Production planning, inventory control, and customer commitments all depend on stable material availability. Disruptions in supply chains can create costly delays and operational stress. Consistent delivery performance and responsive communication help reduce these risks.
Pure nickel strip under DIN 2.4060 and DIN 2.4066 standards continues to serve as a foundational material for precision electronics manufacturing. Its combination of conductivity, formability, and corrosion resistance aligns naturally with the technical and economic priorities of the industry. In practice, successful electronics production is not defined by a single breakthrough technology but by the dependable interaction of materials, processes, and quality control.
For more details, pls directly contact us.


About Us:
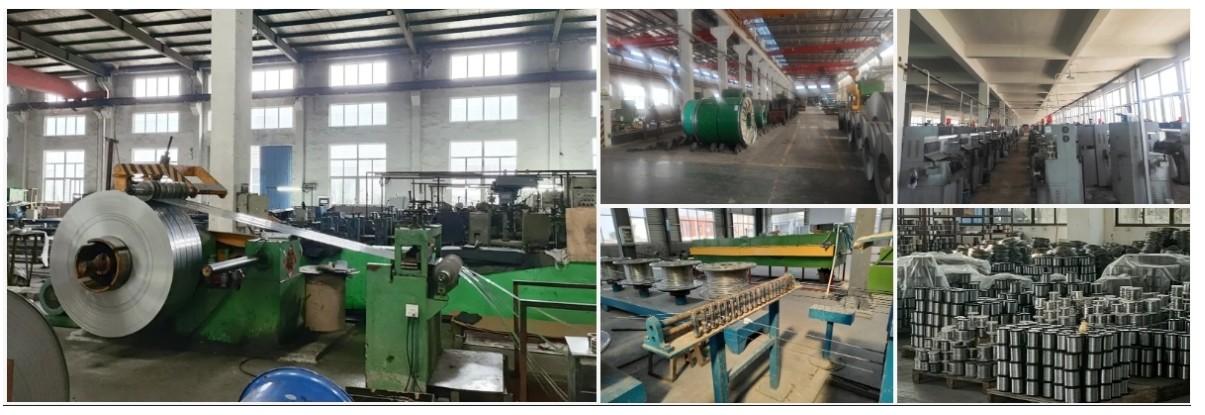
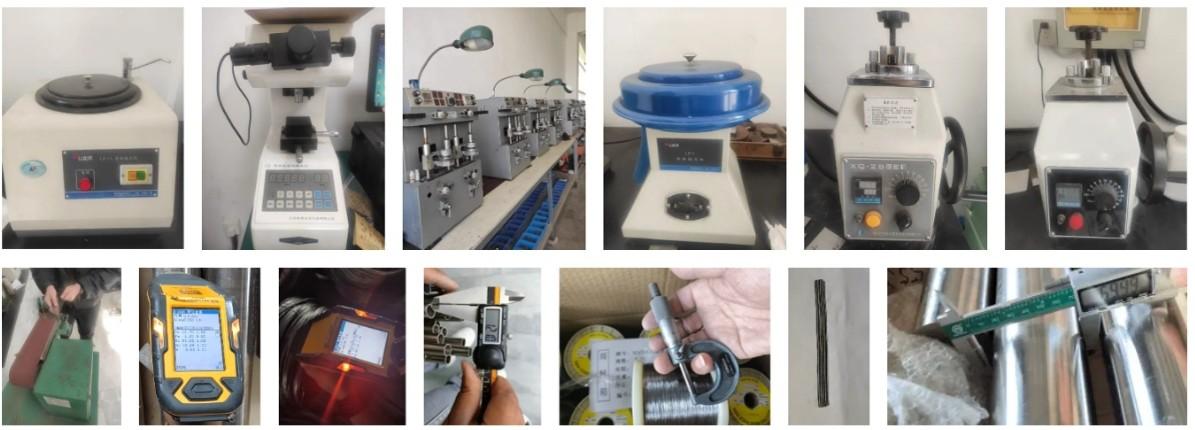
Our 12,000㎡ factory is equipped with complete capabilities for research, production, testing, and packaging. We strictly adhere to ISO 9001 standards in our production processes, with an annual output of 1,200 tons. This ensures that we meet both quantity and quality demands. Furthermore, all products undergo rigorous simulated environment testing including high temperature, high pressure, and corrosion tests before being dispatched, ensuring they meet customer specifications.
For all our clients, we offer timely and multilingual after-sales support and technical consulting, helping you resolve any issues swiftly and efficiently.

Client Visits
Building Stronger Partnerships

We support all kinds of testing:

-
What are DIN 2.4060 and DIN 2.4066 nickel grades?
DIN 2.4060 and DIN 2.4066 are widely recognized German material designations for commercially pure nickel. DIN 2.4060 typically corresponds to Nickel 200 , while DIN 2.4066 aligns with Nickel 201 . Both grades are valued for high nickel content, excellent ductility, stable conductivity, and strong resistance to corrosion. -
Why is pure nickel strip important in precision electronics?
Precision electronics demand materials with predictable electrical performance, dimensional stability, and consistent forming behavior. Pure nickel strip meets these needs by offering reliable conductivity, good mechanical workability, and compatibility with micro-fabrication, stamping, and welding processes. -
How do Nickel 200 and Nickel 201 differ?
The main difference lies in carbon content. Nickel 201 contains lower carbon levels, which improves resistance to intergranular effects at elevated temperatures. For most electronic applications, both grades perform well, but Nickel 201 may be preferred where thermal stability is critical. -
Is pure nickel strip suitable for micro components?
Yes. Pure nickel’s excellent ductility and formability make it ideal for very thin gauges and intricate geometries. It is commonly used in lead frames, connectors, shielding elements, and miniature conductive parts where tight tolerances are essential. -
What manufacturing processes benefit from pure nickel strip?
Pure nickel strip works well with precision stamping, laser cutting, resistance welding, spot welding, and fine forming. Its consistent mechanical behavior helps reduce cracking, deformation issues, and production variability. -
How does nickel strip perform in corrosive environments?
High-purity nickel provides strong resistance to many corrosive conditions, particularly alkaline media. This makes it suitable for electronics exposed to humidity, chemicals, or temperature fluctuations over long service cycles. -
Can thickness and temper be customized?
Yes. Industrial users often require specific thickness ranges, hardness levels, and surface finishes. Pure nickel strip can be supplied in soft annealed or cold rolled conditions, depending on forming and performance requirements. -
What factors matter when choosing an OEM nickel strip supplier?
Consistency, quality control, dimensional accuracy, and long-term supply reliability are key. Precision electronics production relies on materials that behave uniformly across batches, ensuring stable assembly and electrical performance.